Construction and Loss of Bacterial Flagellar Filaments
- PMID: 33182435
- PMCID: PMC7696725
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10111528
Construction and Loss of Bacterial Flagellar Filaments
Abstract
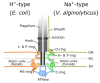
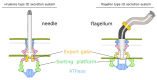
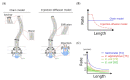
The bacterial flagellar filament is an extracellular tubular protein structure that acts as a propeller for bacterial swimming motility. It is connected to the membrane-anchored rotary bacterial flagellar motor through a short hook. The bacterial flagellar filament consists of approximately 20,000 flagellins and can be several micrometers long. In this article, we reviewed the experimental works and models of flagellar filament construction and the recent findings of flagellar filament ejection during the cell cycle. The length-dependent decay of flagellar filament growth data supports the injection-diffusion model. The decay of flagellar growth rate is due to reduced transportation of long-distance diffusion and jamming. However, the filament is not a permeant structure. Several bacterial species actively abandon their flagella under starvation. Flagellum is disassembled when the rod is broken, resulting in an ejection of the filament with a partial rod and hook. The inner membrane component is then diffused on the membrane before further breakdown. These new findings open a new field of bacterial macro-molecule assembly, disassembly, and signal transduction.
Keywords: flagellar ejection; injection-diffusion model; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Live-Cell Imaging of the Assembly and Ejection Processes of the Bacterial Flagella by Fluorescence Microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2646:35-42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3060-0_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36842104
-
Structure, Assembly, and Function of Flagella Responsible for Bacterial Locomotion.EcoSal Plus. 2023 Dec 12;11(1):eesp00112023. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.esp-0011-2023. Epub 2023 Jun 1. EcoSal Plus. 2023. PMID: 37260402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An intrinsically disordered linker controlling the formation and the stability of the bacterial flagellar hook.BMC Biol. 2017 Oct 27;15(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0438-7. BMC Biol. 2017. PMID: 29078764 Free PMC article.
-
Flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 1996 Jan;19(1):1-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.344874.x. Mol Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8821931 Review.
-
The bacterial flagellum and flagellar motor: structure, assembly and function.Adv Microb Physiol. 1991;32:109-72. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60007-7. Adv Microb Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1882727 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Study.Biomolecules. 2021 May 17;11(5):741. doi: 10.3390/biom11050741. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34067523 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch Complex upon Cell Lysis.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0029821. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00298-21. Epub 2021 Jun 8. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34098733 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizobial Chemotaxis and Motility Systems at Work in the Soil.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Aug 27;12:725338. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.725338. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34512702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of heterologous expression of phaCBA promotes the acetoin stress response mechanism in Bacillus subtilis using transcriptomics and metabolomics approaches.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Feb 21;23(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02334-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38383407 Free PMC article.
-
Risk-reward trade-off during carbon starvation generates dichotomy in motility endurance among marine bacteria.Nat Microbiol. 2025 Jun;10(6):1393-1403. doi: 10.1038/s41564-025-01997-7. Epub 2025 May 26. Nat Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40419768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seishi K., Imai N., Nishitoba M., Sugiyama S., Magariyama Y. Asymmetric swimming pattern of Vibrio alginolyticus cells with single polar flagella. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005;242:221–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

