Molecular Mechanisms of "Antiphospholipid Antibodies" and Their Paradoxical Role in the Pathogenesis of "Seronegative APS"
- PMID: 33182499
- PMCID: PMC7665122
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21218411
Molecular Mechanisms of "Antiphospholipid Antibodies" and Their Paradoxical Role in the Pathogenesis of "Seronegative APS"
Abstract
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by arterial and/or venous thrombosis and/or pregnancy morbidity, associated with circulating antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). In some cases, patients with a clinical profile indicative of APS (thrombosis, recurrent miscarriages or fetal loss), who are persistently negative for conventional laboratory diagnostic criteria, are classified as "seronegative" APS patients (SN-APS). Several findings suggest that aPL, which target phospholipids and/or phospholipid binding proteins, mainly β-glycoprotein I (β-GPI), may contribute to thrombotic diathesis by interfering with hemostasis. Despite the strong association between aPL and thrombosis, the exact pathogenic mechanisms underlying thrombotic events and pregnancy morbidity in APS have not yet been fully elucidated and multiple mechanisms may be involved. Furthermore, in many SN-APS patients, it is possible to demonstrate the presence of unconventional aPL ("non-criteria" aPL) or to detect aPL with alternative laboratory methods. These findings allowed the scientists to study the pathogenic mechanism of SN-APS. This review is focused on the evidence showing that these antibodies may play a functional role in the signal transduction pathway(s) leading to thrombosis and pregnancy morbidity in SN-APS. A better comprehension of the molecular mechanisms triggered by aPL may drive development of potential therapeutic strategies in APS patients.
Keywords: PTMs; SN-APS; TLR-4 pathways; lipid rafts; β2GPI; “non-criteria” aPL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
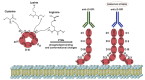
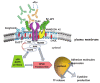

References
-
- Miyakis S., Lockshin M.D., Atsumi T., Branch D.W., Brey R.L., Cervera R., Derksen R.H.W.M., Groot P.G.D.E., Koike T., Meroni P.L., et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01753.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cervera R., Piette J.C., Font J., Khamashta M.A., Shoenfeld Y., Camps M.T., Jacobsen S., Lakos G., Tincani A., Kontopoulou-Griva I., et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome: Clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1000 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1019–1027. doi: 10.1002/art.10187. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yelnik C.M., Urbanski G., Drumez E., Sobanski V., Maillard H., Lanteri A., Morell-Dubois S., Caron C., Dubucquoi S., Launay D., et al. Persistent triple antiphospho lipid antibody positivity as a strong risk factor of frst thrombosis, in a long-term follow-up study of patients without history of thrombosis or obstetrical morbidity. Lupus. 2017;26:163–169. doi: 10.1177/0961203316657433. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

