ER-Localized PIN Carriers: Regulators of Intracellular Auxin Homeostasis
- PMID: 33182545
- PMCID: PMC7697564
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9111527
ER-Localized PIN Carriers: Regulators of Intracellular Auxin Homeostasis
Abstract
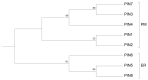
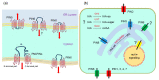
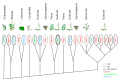
The proper distribution of the hormone auxin is essential for plant development. It is channeled by auxin efflux carriers of the PIN family, typically asymmetrically located on the plasma membrane (PM). Several studies demonstrated that some PIN transporters are also located at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). From the PM-PINs, they differ in a shorter internal hydrophilic loop, which carries the most important structural features required for their subcellular localization, but their biological role is otherwise relatively poorly known. We discuss how ER-PINs take part in maintaining intracellular auxin homeostasis, possibly by modulating the internal levels of IAA; it seems that the exact identity of the metabolites downstream of ER-PINs is not entirely clear as well. We further review the current knowledge about their predicted structure, evolution and localization. Finally, we also summarize their role in plant development.
Keywords: ER-PINs; PIN proteins; PIN5; PIN8; auxin metabolism; auxin transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zažímalová E., Petrášek J., Benková E., editors. Auxin and Its Role in Plant Development. Springer; Vienna, Austria: 2014.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

