Neuroticism predicts informant reported cognitive problems through health behaviors
- PMID: 33183066
- PMCID: PMC8767481
- DOI: 10.1080/13607863.2020.1839857
Neuroticism predicts informant reported cognitive problems through health behaviors
Abstract
Objective: Personality traits have been linked to cognitive impairment, though work is needed to understand the mechanisms involved. Research also needs to consider alternative markers of cognitive impairment, such as informant report measures. The aim of the current study was to examine the role of health behaviors and social engagement as mediators for the relationship between personality and informant reported cognitive problems. It was expected that neuroticism would predict cognitive problems through negative health behaviors, while conscientiousness might predict cognitive problems through positive health behaviors.
Methods: Using data from the St. Louis Personality and Aging Network study at three time points, spanning approximately 2.27 years (N = 829, M age = 65.95), correlations were computed between the Big Five personality traits and health behaviors at wave 1, social engagement at wave 2, and informant reported cognitive problems at wave 3. Mediation tests examined whether health behaviors and social engagement explained the relationships found between personality and informant reported cognitive problems.
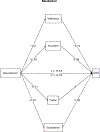
Results: Findings showed that neuroticism at wave 1 significantly predicted informant reported cognitive problems at wave 3 and that health behaviors, specifically wellness maintenance, partially explained this relationship. No significant associations were found between informant reported cognitive problems and conscientiousness, agreeableness, extraversion, openness, or social engagement.
Conclusion: This study supports claims that neuroticism predicts later cognitive problems and expands on previous literature by demonstrating this relationship using an informant report measure. Furthermore, we found that health behaviors, and specifically wellness maintenance, account for some of the relationship between neuroticism and informant reported cognitive problems.
Keywords: Psychological and social aspects; age associated memory problems; cognitive functioning.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2019a). Facts and Figures Retrieved from https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures.
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2019b). Cognitive Assessment Retrieved from www.alz.org/professionals/health-systems-clinicians/cognitive-assessment.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources