Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals evolutionary divergence and shared network of cold and salt stress response in diploid D-genome cotton
- PMID: 33183239
- PMCID: PMC7664088
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-020-02726-4
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals evolutionary divergence and shared network of cold and salt stress response in diploid D-genome cotton
Abstract
Background: Wild species of cotton are excellent resistance to abiotic stress. Diploid D-genome cotton showed abundant phenotypic diversity and was the putative donor species of allotetraploid cotton which produce the largest textile natural fiber.
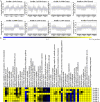
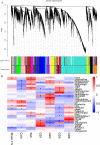
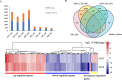
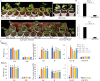
Results: A total of 41,053 genes were expressed in all samples by mapping RNA-seq Illumina reads of G. thurberi (D1), G. klotzschianum (D3-k), G. raimondii (D5) and G. trilobum (D8) to reference genome. The numbers of differently expressed genes (DEGs) were significantly higher under cold stress than salt stress. However, 34.1% DEGs under salt stress were overlapped with cold stress in four species. Notably, a potential shared network (cold and salt response, including 16 genes) was mined out by gene co-expression analysis. A total of 47,180-55,548 unique genes were identified in four diploid species by De novo assembly. Furthermore, 163, 344, 330, and 161 positively selected genes (PSGs) were detected in thurberi, G. klotzschianum, G. raimondii and G. trilobum by evolutionary analysis, respectively, and 9.5-17% PSGs of four species were DEGs in corresponding species under cold or salt stress. What's more, most of PSGs were enriched GO term related to response to stimulation. G. klotzschianum showed the best tolerance under both cold and salt stress. Interestingly, we found that a RALF-like protein coding gene not only is PSGs of G. klotzschianum, but also belongs to the potential shared network.
Conclusion: Our study provided new evidence that gene expression variations of evolution by natural selection were essential drivers of the morphological variations related to environmental adaptation during evolution. Additionally, there exist shared regulated networks under cold and salt stress, such as Ca2+ signal transduction and oxidation-reduction mechanisms. Our work establishes a transcriptomic selection mechanism for altering gene expression of the four diploid D-genome cotton and provides available gene resource underlying multi-abiotic resistant cotton breeding strategy.
Keywords: Co-expression; Comparative transcriptome; Diploid D-genome cotton; Evolutionary divergence; Shared network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no any form of competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Paterson AH, Wendel JF, Gundlach H, Guo H, Jenkins J, Jin D, Llewellyn D, Showmaker KC, Shu S, Udall J, Yoo M, Byers R, Chen W, Doron-Faigenboim A, Duke MV, Gong L, Grimwood J, Grover C, Grupp K, Hu G, Lee T, Li J, Lin L, Liu T, Marler BS, Page JT, Roberts AW, Romanel E, Sanders WS, Szadkowski E, Tan X, Tang H, Xu C, Wang J, Wang Z, Zhang D, Zhang L, Ashrafi H, Bedon F, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chee PW, Das S, Gingle AR, Haigler CH, Harker D, Hoffmann LV, Hovav R, Jones DC, Lemke C, Mansoor S, Rahman Mu, Rainville LN, Rambani A, Reddy UK, Rong J-K, Saranga Y, Scheffler BE, Scheffler JA, Stelly DM, Triplett BA, Deynze AV, Vaslin MFS, Waghmare VN, Walford SA, Wright RJ, Zaki EA, Zhang T, Dennis ES, Mayer KFX, Peterson DG, Rokhsar DS, Wang X, Schmutz J. Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature. 2012;492(7429):423-7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

