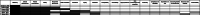Assessing hospital performance indicators. What dimensions? Evidence from an umbrella review
- PMID: 33183304
- PMCID: PMC7663881
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-020-05879-y
Assessing hospital performance indicators. What dimensions? Evidence from an umbrella review
Abstract
Background: Patients' increasing needs and expectations require an overall assessment of hospital performance. Several international agencies have defined performance indicators sets but there exists no unanimous classification. The Impact HTA Horizon2020 Project wants to address this aspect, developing a toolkit of key indicators to measure hospital performance. The aim of this review is to identify and classify the dimensions of hospital performance indicators in order to develop a common language and identify a shared evidence-based way to frame and address performance assessment.
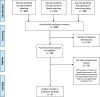
Methods: Following the PRISMA statement, PubMed, Cochrane Library and Web of Science databases were queried to perform an umbrella review. Reviews focusing on hospital settings, published January 2000-June 2019 were considered. The quality of the studies selected was assessed using the AMSTAR2 tool.
Results: Six reviews ranging 2002-2014 were included. The following dimensions were described in at least half of the studies: 6 studies classified efficiency (55 indicators analyzed); 5 studies classified effectiveness (13 indicators), patient centeredness (10 indicators) and safety (8 indicators); 3 studies responsive governance (2 indicators), staff orientation (10 indicators) and timeliness (4 indicators). Three reviews did not specify the indicators related to the dimensions listed, and one article gave a complete definition of the meaning of each dimension and of the related indicators.
Conclusions: The research shows emphasis of the importance of patient centeredness, effectiveness, efficiency, and safety dimensions. Especially, greater attention is given to the dimensions of effectiveness and efficiency. Assessing the overall quality of clinical pathways is key in guaranteeing a truly effective and efficient system but, to date, there still exists a lack of awareness and proactivity in terms of measuring performance of nodes within networks. The effort of classifying and systematizing performance measurement techniques across hospitals is essential at the organizational, regional/national and possibly international levels to deliver top quality care to patients.
Keywords: Hospital evaluation; Hospital performance; Indicator; Performance dimensions; Performance measurement; Quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Busse R, Klazinga N, Panteli D, Quentin W. Improving healthcare quality in Europe. Characteristics, effectiveness and implementation of different strategies. WHO-European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies and OECD: United Kingdom; 2019. - PubMed
-
- Handbook for national quality policy and strategy . a practical approach for developing policy and strategy to improve quality of care. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical