Long-term outcome after combined kyphoplasty and intraoperative radiotherapy (Kypho-IORT) for vertebral tumors
- PMID: 33183307
- PMCID: PMC7664102
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-020-01715-z
Long-term outcome after combined kyphoplasty and intraoperative radiotherapy (Kypho-IORT) for vertebral tumors
Abstract
Introduction: The spine represents the site which is most frequently affected by bone metastases in patients with systemic cancer. Of all local treatment options, combined kyphoplasty and intraoperative radiotherapy (Kypho-IORT) provides both, instantaneous stabilization and immediate pain relief. We here report on the long-term outcomes of the largest cohort treated with Kypho-IORT to date.
Methods: Between 2009 and 2019 a total of 104 patients underwent Kypho-IORT to vertebral tumors in the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral spine with transpedicular kyphoplasty and intraoperative irradiation with a needle-shaped electronic brachytherapy source at our center. Patients were treated either on trial, within the prospective Kypho-IORT studies (NCT01280032 and NCT02773966), or, after completion of the study, off trial but compliant with the study protocol. Follow-up and imaging with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging was scheduled after 3 and 6 months and then bi-annually.
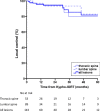
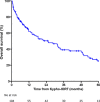
Results: A total of 143 vertebrae (89 thoracic spine, 53 lumbar spine, and 1 sacral spine) were treated in 104 patients. The median follow-up was 14.5 months (range 0.4-109). Local progression occurred in 10 patients (10 vertebrae) after a median time of 22.3 months (range 1.5-73) resulting in local control rates of 97.1, 95.9, and 94.2% at 6, 12, and 24 months, respectively. Overall survival was 74.6, 61.7, and 50.3% at 6, 12, and 24 months, respectively. A single serious adverse event was reported.
Conclusion: In addition to immediate pain reduction and stabilization, Kypho-IORT shows excellent long-term local control with minimal side effects.
Keywords: Electronic brachytherapy; Intraoperative radiotherapy; Kypho-IORT; Kyphoplasty; Spine; Vertebral metastases.
Conflict of interest statement
LW, GW, UO, FW and AMR have no competing interests to disclose. FB and FS report grants and personal fees from Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, during the conduct of the study; FG reports grants, personal fees, and patents from or related to Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, grants from Elekta AB; grants and personal fees from NOXXON Pharma AG, personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Roche Pharma AG, personal fees from MSD Sharp and Dohme GmbH, personal fees from AstraZeneca GmbH, non-financial support from Oncare GmbH, outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Huvos AG. Bone tumors: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. 2. New York: W.B. Saunders Company and Cbs Educational and Professional Publishing; 1987.
-
- Berenson J, Pflugmacher R, Jarzem P, Zonder J, Schechtman K, Tillman JB, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty versus non-surgical fracture management for treatment of painful vertebral body compression fractures in patients with cancer: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70008-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

