Analysis of a persistent viral shedding patient infected with SARS-CoV-2 by RT-qPCR, FilmArray Respiratory Panel v2.1, and antigen detection
- PMID: 33183963
- PMCID: PMC7598429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.10.026
Analysis of a persistent viral shedding patient infected with SARS-CoV-2 by RT-qPCR, FilmArray Respiratory Panel v2.1, and antigen detection
Abstract
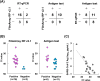
Various diagnostic tests utilizing different principles are currently under development for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). However, these tests can occasionally produce discrepant results, causing confusion in their interpretation. Here, we evaluated the performance and features of three diagnostic assays: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), FilmArray Respiratory Panel (RP) v2.1, and the LUMIPULSE antigen test. Twenty-seven serial nasopharyngeal swabs were collected from a prolonged viral shedding patient who had been hospitalized for 51 days. We examined the SARS-CoV-2 detection rates of the three tests. The overall agreement rate was 81% between RT-qPCR and FilmArray RP v2.1, 63% between the antigen test and FilmArray RP v2.1, and 59% between the antigen test and RT-qPCR. We obtained concordant results in samples with high viral loads (low threshold cycle values) by all three tests. RT-qPCR and FilmArray RP v2.1 accurately detected SARS-CoV-2 at the early to intermediate phases of infection, but the results varied at the late phase. The antigen test also produced a positive result at the early phase but varied at the intermediate phase and consistently produced negative results at late phase of infection. These results demonstrated FilmArray RP v2.1 could detect SARS-CoV-2 with accuracy comparable to RT-qPCR. Further, there were discrepant results using different types of diagnostic tests during the clinical course of prolonged viral shedding patient. We provided insights into how to utilize different types of kits to assess and manage SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Keywords: Antigen; COVID-19; FilmArray; RT-qPCR; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Organization W.H. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation reports. https://wwwwhoint/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-...
-
- Hirotsu Y., Maejima M., Nakajima M., Mochizuki H., Omata M. Environmental cleaning is effective for the eradication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in contaminated hospital rooms: a patient from the Diamond Princess cruise ship. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020;41(9):1105–1106. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

