The diagnostic value of DNA repair gene in breast cancer metastasis
- PMID: 33184404
- PMCID: PMC7661505
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-76577-2
The diagnostic value of DNA repair gene in breast cancer metastasis
Abstract
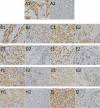
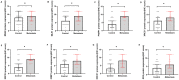
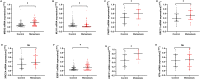
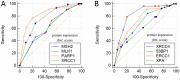
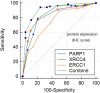
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in China and even in the world. DNA repair genes can lead to tumor metastasis by affecting cancer cell resistance. Studies have preliminarily shown that DNA repair genes are related to breast cancer metastasis, but it is not clear whether they can be used as a prediction of the risk of breast cancer metastasis. Therefore, this study mainly discusses the predictive value of DNA repair genes in postoperative metastasis of breast cancer. The nested case-control method was used in patients with breast cancer metastasis after surgery (n = 103) and patients without metastasis after surgery (n = 103). The proteins and mRNA of DNA repair genes were detected by immunohistochemistry and Real-time PCR respectively. In protein expression, PARP1 (OR 1.147, 95% CI 1.067 ~ 1.233, P < 0.05), XRCC4 (OR 1.088, 95% CI 1.015 ~ 1.166, P < 0.05), XRCC1 (OR 1.114, 95% CI 1.021 ~ 1.215, P < 0.05), ERCC1 (OR 1.068, 95% CI 1.000 ~ 1.141, P < 0.10) were risk factors for postoperative metastasis of breast cancer. In addition, we used the ROC curve to study the optimal critical values of MSH2, MLH1, PARP1, XRCC1, XRCC4, 53BP1, ERCC1 and XPA combined with the Youden index, and the effects of MSH2, MLH1, PARP1, XRCC1, XRCC4, 53BP1, ERCC1 and XPA on breast cancer metastasis were verified again. Among them, the risk of metastasis in the PARP1 high expression group was 3.286 times that of the low expression group (OR 3.286, 95% CI 2.013 ~ 5.364, P < 0.05). The risk of metastasis in the XRCC4 high expression group was 1.779 times that of the low expression group (OR 1.779, 95% CI 1.071 ~ 2.954, P < 0.05). The risk of metastasis in patients with ERCC1 high expression group was 2.012 times that of the low expression group (OR 2.012, 95% CI 1.056 ~ 3.836, P < 0.05). So we can conclude that protein expression of PARP1 (cut-off value = 6, Se = 76.70%, Sp = 79.61%), XRCC4 (cut-off value = 6, Se = 78.64%0, Se = 79.61%), ERCC1 (cut-off value = 3, Se = 89.32%, Sp = 50.49%), suggesting that when the PARP1 score is higher than 6 or the XRCC4 score is higher than 6 or the ERCC1 score is higher than 3, the risk of metastasis will increases. Due to PARP1, XRCC4 and ERCC1 belong to a part of DNA repair gene system, and the three proteins are positively correlated by correlation analysis (rPARP1-XRCC4 = 0.343; rPAPR1-ERCC1 = 0.335; rXRCC4-ERCC1 = 0.388). The combined diagnosis of the PARR1, XRCC4 and ERCC1 have greater predictive value for the risk of metastasis of breast cancer (Se = 94.17%, Sp = 75.73%; OR 11.739, 95% CI 2.858 ~ 40.220, P < 0.05). The postoperative metastasis of breast cancer could be effectively predicted when the immunohistochemical scores met PARP1 (IHC score) > 6, XRCC4 (IHC score) > 6 and ERCC1 (IHC score) > 3. In addition, the combined diagnosis of PARP1, XRCC4 and ERCC1 has great predictive value for the risk of breast cancer metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Value of the NF-κB signalling pathway and the DNA repair gene PARP1 in predicting distant metastasis after breast cancer surgery.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 22;14(1):4402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49156-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38388665 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of ERCC1, MSH2 and PARP1 in non-small cell lung cancer and prognostic value in patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(6):2591-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.6.2591. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24761869
-
Association of expression of p53, livin, ERCC1, BRCA1 and PARP1 in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue with drug resistance and prognosis.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Feb;216(2):152794. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152794. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 31902551
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer in patients from Southern China.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8312-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERCC1: impact in multimodality treatment of upper gastrointestinal cancer.Future Oncol. 2010 Nov;6(11):1735-49. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.140. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21142660 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Neoantigen Expression and T-Cell Activation on Breast Cancer Survival.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;13(12):2879. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122879. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207556 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer Patients: A Balancing Act between Stemness, EMT Features and DNA Damage Responses.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 16;14(4):997. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040997. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERCC1/NGFR affects prognosis in basal-like breast cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 9;30(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02807-w. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40629424 Free PMC article.
-
MSLN induced EMT, cancer stem cell traits and chemotherapy resistance of pancreatic cancer cells.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 7;10(8):e29210. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29210. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38628720 Free PMC article.
-
Value of the NF-κB signalling pathway and the DNA repair gene PARP1 in predicting distant metastasis after breast cancer surgery.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 22;14(1):4402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49156-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38388665 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

