Predicting High Coronary Artery Calcium Score From Retinal Fundus Images With Deep Learning Algorithms
- PMID: 33184590
- PMCID: PMC7410115
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.2.28
Predicting High Coronary Artery Calcium Score From Retinal Fundus Images With Deep Learning Algorithms
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate high accumulation of coronary artery calcium (CAC) from retinal fundus images with deep learning technologies as an inexpensive and radiation-free screening method.
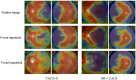
Methods: Individuals who underwent bilateral retinal fundus imaging and CAC score (CACS) evaluation from coronary computed tomography scans on the same day were identified. With this database, performances of deep learning algorithms (inception-v3) to distinguish high CACS from CACS of 0 were evaluated at various thresholds for high CACS. Vessel-inpainted and fovea-inpainted images were also used as input to investigate areas of interest in determining CACS.
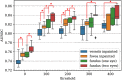
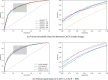
Results: A total of 44,184 images from 20,130 individuals were included. A deep learning algorithm for discrimination of no CAC from CACS >100 achieved area under receiver operating curve (AUROC) of 82.3% (79.5%-85.0%) and 83.2% (80.2%-86.3%) using unilateral and bilateral fundus images, respectively, under a 5-fold cross validation setting. AUROC increased as the criterion for high CACS was increased, showing a plateau at 100 and losing significant improvement thereafter. AUROC decreased when fovea was inpainted and decreased further when vessels were inpainted, whereas AUROC increased when bilateral images were used as input.
Conclusions: Visual patterns of retinal fundus images in subjects with CACS > 100 could be recognized by deep learning algorithms compared with those with no CAC. Exploiting bilateral images improves discrimination performance, and ablation studies removing retinal vasculature or fovea suggest that recognizable patterns reside mainly in these areas.
Translational relevance: Retinal fundus images can be used by deep learning algorithms for prediction of high CACS.
Keywords: coronary artery calcium score; deep learning; retinal fundus images.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: J. Son, VUNO (E); J.Y. Shin, None; E.J. Chun, None; K.-H. Jung, VUNO (I, E); K.H. Park, None; S.J. Park, VUNO (I)
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting categories of coronary artery calcium scores from chest X-ray images using deep learning.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2025 May-Jun;19(3):331-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2025.03.010. Epub 2025 Apr 7. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2025. PMID: 40199634
-
Prediction of Coronary Artery Calcium Score Using Machine Learning in a Healthy Population.J Pers Med. 2020 Aug 20;10(3):96. doi: 10.3390/jpm10030096. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32825442 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of Deep Learning Models for Screening Multiple Abnormal Findings in Retinal Fundus Images.Ophthalmology. 2020 Jan;127(1):85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.05.029. Epub 2019 May 31. Ophthalmology. 2020. PMID: 31281057
-
Deep learning algorithms for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Jul;191:105320. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105320. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32088490
-
Machine Learning and Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020 Jul 9;22(9):90. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-01337-7. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647932 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Learning Algorithms for Screening and Diagnosis of Systemic Diseases Based on Ophthalmic Manifestations: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;13(5):900. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050900. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertensive eye disease.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022 Mar 10;8(1):14. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00342-0. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022. PMID: 35273180 Review.
-
High-resolution fundus images for ophthalmomics and early cardiovascular disease prediction.Sci Data. 2025 Apr 3;12(1):568. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04930-z. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40180990 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based fundus image analysis for cardiovascular disease: a review.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023 Nov 18;14:20406223231209895. doi: 10.1177/20406223231209895. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023. PMID: 38028950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Predicting Systemic Parameters and Diseases From Ophthalmic Imaging.Front Digit Health. 2022 May 26;4:889445. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2022.889445. eCollection 2022. Front Digit Health. 2022. PMID: 35706971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang SB, Mitchell P, Liew G, et al. .. A spectrum of retinal vasculature measures and coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2018; 268: 215–224. - PubMed
-
- Liew G, Benitez-Aguirre P, Craig ME, et al. .. Progressive Retinal Vasodilation in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: A Longitudinal Study of Retinal Vascular Geometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017; 58: 2503–2509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

