Volume overload in hemodialysis: diagnosis, cardiovascular consequences, and management
- PMID: 33184659
- PMCID: PMC8643589
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa182
Volume overload in hemodialysis: diagnosis, cardiovascular consequences, and management
Abstract
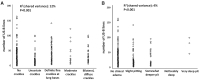
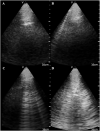
Volume overload in haemodialysis (HD) patients associates with hypertension and cardiac dysfunction and is a major risk factor for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in this population. The diagnosis of volume excess and estimation of dry weight is based largely on clinical criteria and has a notoriously poor diagnostic accuracy. The search for accurate and objective methods to evaluate dry weight and to diagnose subclinical volume overload has been intensively pursued over the last 3 decades. Most methods have not been tested in appropriate clinical trials and their usefulness in clinical practice remains uncertain, except for bioimpedance spectroscopy and lung ultrasound (US). Bioimpedance spectroscopy is possibly the most widely used method to subjectively quantify fluid distributions over body compartments and produces reliable and reproducible results. Lung US provides reliable estimates of extravascular water in the lung, a critical parameter of the central circulation that in large part reflects the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure. To maximize cardiovascular tolerance, fluid removal in volume-expanded HD patients should be gradual and distributed over a sufficiently long time window. This review summarizes current knowledge about the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of volume overload in HD patients.
Keywords: bioimpedance analysis; dry weight; haemodialysis; lung ultrasound; volume overload.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- de Jager DJ, Grootendorst DC, Jager KJ, et al. Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA 2009; 302: 1782–1789 - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Gilbertson DT, Murray T, et al. Long interdialytic interval and mortality among patients receiving hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 2011; 365: 1099–1107 - PubMed
-
- Sarafidis PA, Persu A, Agarwal R, et al. Hypertension in dialysis patients: a consensus document by the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine (EURECA-m) working group of the European Renal Association–European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) and the Hypertension and the Kidney working group of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017; 32: 620–640 - PubMed
-
- Loutradis CN, Tsioufis C, Sarafidis PA. The clinical problems of hypertension treatment in hemodialysis patients. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2017; 16: 54–60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical