Influence of bacterial components on the developmental programming of enteric neurons
- PMID: 33185323
- PMCID: PMC7663985
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14611
Influence of bacterial components on the developmental programming of enteric neurons
Abstract
Background: Intestinal bacteria have been increasingly shown to be involved in early postnatal development. Previous work has shown that intestinal bacteria are necessary for the structural development and intrinsic function of the enteric nervous system in early postnatal life. Furthermore, colonization with a limited number of bacteria appears to be sufficient for the formation of a normal enteric nervous system. We tested the hypothesis that common bacterial components could influence the programming of developing enteric neurons.
Methods: The developmental programming of enteric neurons was studied by isolating enteric neural crest-derived cells from the fetal gut of C57Bl/6 mice at embryonic day 15.5. After the establishment of the cell line, cultured enteric neuronal precursors were exposed to increasing concentrations of a panel of bacterial components including lipopolysaccharide, flagellin, and components of peptidoglycan.
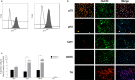
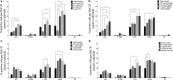
Key result: Exposure to bacterial components consistently affected proportions of enteric neuronal precursors that developed into nitrergic neurons. Furthermore, flagellin and D-gamma-Glu-mDAP were found to promote the development of serotonergic neurons. Proportions of dopaminergic neurons remained unchanged. Proliferation of neuronal precursor cells was significantly increased upon exposure to lipopolysaccharide and flagellin, while no significant changes were observed in the proportion of apoptotic neuronal precursors compared to baseline with exposure to any bacterial component.
Conclusions and interfaces: These findings suggest that bacterial components may influence the development of enteric neurons.
Keywords: bacterial components; development; enteric nervous system; enteric neural crest-derived cells.
© 2020 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors wish to declare no conflicts of interest relevant to the conducted research.
Figures
References
-
- Akamatsu, W. , Fujihara, H. , Mitsuhashi, T. , Yano, M. , Shibata, S. , Hayakawa, Y. , …, Okano, H. (2005). The RNA‐binding protein HuD regulates neuronal cell identity and maturation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(12), 4625–4630. 10.1073/pnas.0407523102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anitha, M. , Reichardt, F. , Tabatabavakili, S. , Nezami, B. G. , Chassaing, B. , Mwangi, S. , …, Srinivasan, S. (2016). Intestinal dysbiosis contributes to the delayed gastrointestinal transit in high‐fat diet fed mice. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2(3), 328–339. 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.12.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

