Comparison of Binding Site of Remdesivir and Its Metabolites with NSP12-NSP7-NSP8, and NSP3 of SARS CoV-2 Virus and Alternative Potential Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment
- PMID: 33185784
- PMCID: PMC7662030
- DOI: 10.1007/s10930-020-09942-9
Comparison of Binding Site of Remdesivir and Its Metabolites with NSP12-NSP7-NSP8, and NSP3 of SARS CoV-2 Virus and Alternative Potential Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment
Abstract
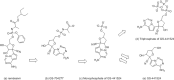
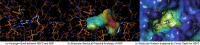
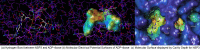
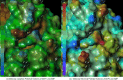
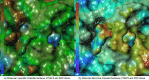
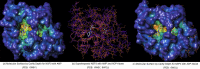
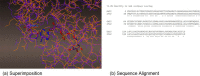
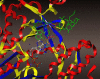
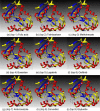
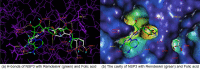
Remdesivir was approved by the U.S.A. Food and Drug administration for emergency use to interfere with the replication of SARS CoV-2 virus (the agent that causes COVID-19) in adults and children hospitalized with severe disease. The crystal structure of the metabolite of remdesivir (Monophosphate of GS-441524) and NSP12-NSP8-NSP7 of SARS CoV-2 virus was recently reported. The crystal structures of ADP-Ribose or AMP and NSP3 of SARS CoV-2 virus were also released, recently. This study compared their binding sites and suggests the crystal structure of NSP3 of SARS CoV-2 virus as an alternative binding site of AMP or ADP-ribose to treat COVID-19. We virtually screened 682 FDA-approved compounds, and the top 10 compounds were selected by analysis of docking scores, (G-score, D-score, and Chemscore) and visual analysis using a structure-based docking approach of NSP3 of SARS CoV-2 virus. All immunization approaches are based on the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein. A recent study reported that the D614G mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein reduces S1 shedding and increases infectivity of SARS COV-2 virus. Therefore, if there is a severe change in the spike protein of a modified Coronavirus, all developed vaccines can lose their efficacy, necessitating the need for an alternative treatment method. The top 10 compounds (FDA-approved) in this study are selected based on NSP 3 binding site, and therefore are a potential viable treatment because they will show potential activity for all mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein.
Keywords: Non-structural protein 3 (NSP3) of SARS CoV-2 virus; Remdesivir; Virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Longitudinal analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase protein sequences reveals the emergence and geographic distribution of diverse mutations.Infect Genet Evol. 2022 Jan;97:105153. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105153. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Infect Genet Evol. 2022. PMID: 34801754 Free PMC article.
-
Theaflavin-3'-O-gallate a Black-tea Constituent Blocked SARS CoV-2 RNA dependant RNA Polymerase Active-site with Better Docking Results than Remdesivir.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2021 Oct;71(8):462-472. doi: 10.1055/a-1467-5828. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2021. PMID: 34517419
-
Piece of the puzzle: Remdesivir disassembles the multimeric SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complex.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Jun;79(2):175-187. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-00977-y. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33792836 Free PMC article.
-
Remdesivir: Quo vadis?Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;193:114800. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114800. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34678228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: Structure, mechanism, and drug discovery for COVID-19.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.116. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 32943188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inspection on the Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 Inhibition by Penciclovir: A Molecular Dynamic Study.Molecules. 2022 Dec 26;28(1):191. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010191. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615385 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the development of antiviral against Mayaro virus: from molecules to potential viral targets.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Mar 7;205(4):106. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03441-y. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36881172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of potential inhibitors targeting non-structural proteins 3 (PLpro and Mac1) and 5 (3CLpro/Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:4868-4883. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.08.036. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34457214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 in Children: A Review.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Nov 12;14:8097-8108. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S335888. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34795516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and immunogenicity of non-structural protein 8 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus.Vet Res Forum. 2024;15(2):65-73. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2023.2009322.3977. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Vet Res Forum. 2024. PMID: 38465319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stephens B (2020) The story of remdesivir. The New York Times https://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/17/opinion/remdesivir-coronavirus.html. Accessed 21 Sept 2020
-
- Warren TK, Jordan R, Lo MK, Ray AS, Mackman RL, Soloveva V, Siegel D, Perron M, Bannister R, Hui HC, Larson N, Strickley R, Wells J, Stuthman KS, Van Tongeren SA, Garza NL, Donnelly G, Shurtleff AC, Retterer CJ, Gharaibeh D, Zamani R, Kenny T, Eaton BP, Grimes E, Welch LS, Gomba L, Wilhelmsen CL, Nichols DK, Nuss JE, Nagle ER, Kugelman JR, Palacios G, Doerffler E, Neville S, Carra E, Clarke MO, Zhang L, Lew W, Ross B, Wang Q, Chun K, Wolfe L, Babusis D, Park Y, Stray KM, Trancheva I, Feng JY, Barauskas O, Xu Y, Wong P, Braun MR, Flint M, McMullan LK, Chen SS, Fearns R, Swaminathan S, Mayers DL, Spiropoulou CF, Lee WA, Nichol ST, Cihlar T, Bavari S. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature. 2016;7594:381–385. doi: 10.1038/nature17180. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yin W, Mao C, Luan X, Hou F, Zhao W, Gao M, Chang S, Xie Y, Tian G, Jiang H, Tao S, Shen J, Jiang Y, Jiang H, Xu Y, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Xu HE. Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir. Science. 2020;368:1499–1504. doi: 10.1126/science.abc1560. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

