Interleukin-8 Receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 Are Not Expressed by Endothelial Colony-forming Cells
- PMID: 33185837
- PMCID: PMC8337095
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-020-10081-y
Interleukin-8 Receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 Are Not Expressed by Endothelial Colony-forming Cells
Abstract
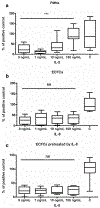
Endothelial colony-forming cells (ECFCs) are human vasculogenic cells described as potential cell therapy product and good candidates for being a vascular liquid biopsy. Since interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a main actor in senescence, its ability to interact with ECFCs has been explored. However, expression of CXCR1 and CXCR2, the two cellular receptors for IL-8, by ECFCs remain controversial as several teams published contradictory reports. Using complementary technical approaches, we have investigated the presence of these receptors on ECFCs isolated from cord blood. First, CXCR1 and CXCR2 were not detected on several clones of cord blood- endothelial colony-forming cell using different antibodies available, in contrast to well-known positive cells. We then compared the RT-PCR primers used in different papers to search for the presence of CXCR1 and CXCR2 mRNA and found that several primer pairs used could lead to non-specific DNA amplification. Last, we confirmed those results by RNA sequencing. CXCR1 and CXCR2 were not detected in ECFCs in contrary to human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells (h-iECs). In conclusion, using three different approaches, we confirmed that CXCR1 and CXCR2 were not expressed at mRNA or protein level by ECFCs. Thus, IL-8 secretion by ECFCs, its effects in angiogenesis and their involvement in senescent process need to be reanalyzed according to this absence of CXCR-1 and - 2 in ECFCs.Graphical Abstract.
Keywords: CXCR1; CXCR2; ECFCs; RNAseq; chemokines; interleukin-8.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Smadja DM (2019). Vasculogenic stem and progenitor cells in human: future cell therapy product or liquid biopsy for vascular disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1201, 215–237. - PubMed
-
- Medina RJ, O’Neill CL, O’Doherty TM, et al. (2013). Ex vivo expansion of human outgrowth endothelial cells leads to IL-8-mediated replicative senescence and impaired vasoreparative function: IL8 mediates OEC senescence. Stem Cells, 31(8), 1657–1668. - PubMed
-
- Blandinières A, Gendron N, Bacha N, et al. (2019). Interleukin-8 release by endothelial colony-forming cells isolated from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients might contribute to their pathogenicity. Angiogenesis, 22(2), 325–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

