Cisplatin Prodrug-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Physalis Mottle Virus for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 33186039
- PMCID: PMC8087187
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00834
Cisplatin Prodrug-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Physalis Mottle Virus for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
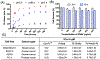
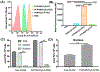
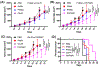
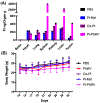
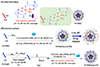
Nanoparticle-based prodrugs offer an effective strategy to improve the safety and delivery of small-molecule therapeutics while reducing the risk of drug resistance. Here, we conjugated a maleimide-functionalized cisplatin prodrug containing Pt(IV) to the internal and/or external surface of virus-like particles (VLPs) derived from Physalis mottle virus (PhMV) to develop a pH-sensitive drug delivery system. The internally loaded and PEGylated VLPs (Pt-PhMVCy5.5-PEG) were taken up efficiently by cancer cells where they released platinum, presumably as a reduced, DNA-reactive Pt(II) complex, rapidly under acidic conditions in vitro (>80% in 30 h). The efficacy of the VLP-based drug delivery system was demonstrated against a panel of cancer cell lines, including cell lines resistant to platinum therapy. Furthermore, Pt-PhMVCy5.5-PEG successfully inhibited the growth of xenograft MDA-MB-231 breast tumors in vivo and significantly prolonged the survival of mice compared to free cisplatin and cisplatin-maleimide. Pt-PhMVCy5.5-PEG therefore appears promising as a prodrug to overcome the limitations of conventional platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy.
Keywords: cisplatin resistance; nanomedicine; pH-responsive drug delivery; plant virus-like nanoparticles; prodrug.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-... (03/26/2020),
-
- Pushpakom S; Iorio F; Eyers PA; Escott KJ; Hopper S; Wells A; Doig A; Guilliams T; Latimer J; McNamee C; Norris A; Sanseau P; Cavalla D; Pirmohamed M Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2018, 18, 41–58. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg. Chem 2019, 88, 102925. - PubMed
-
- Wang D; Lippard SJ Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 2005, 4, 307–320. - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L; Senovilla L; Vitale I; Michels J; Martins I; Kepp O; Castedo M; Kroemer G Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

