Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteases and Polymerase for COVID-19 Treatment: State of the Art and Future Opportunities
- PMID: 33186044
- PMCID: PMC7688049
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01140
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteases and Polymerase for COVID-19 Treatment: State of the Art and Future Opportunities
Abstract
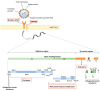
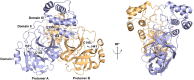
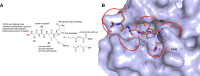
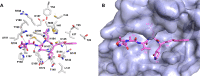
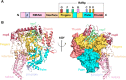
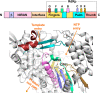
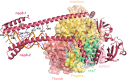
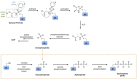
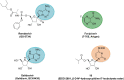
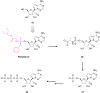
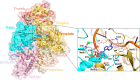
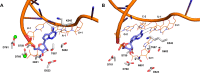
The newly emerged coronavirus, called SARS-CoV-2, is the causing pathogen of pandemic COVID-19. The identification of drugs to treat COVID-19 and other coronavirus diseases is an urgent global need, thus different strategies targeting either virus or host cell are still under investigation. Direct-acting agents, targeting protease and polymerase functionalities, represent a milestone in antiviral therapy. The 3C-like (or Main) protease (3CLpro) and the nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) are the best characterized SARS-CoV-2 targets and show the highest degree of conservation across coronaviruses fostering the identification of broad-spectrum inhibitors. Coronaviruses also possess a papain-like protease, another essential enzyme, still poorly characterized and not equally conserved, limiting the identification of broad-spectrum agents. Herein, we provide an exhaustive comparative analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteases and RdRp with respect to other coronavirus homologues. Moreover, we highlight the most promising inhibitors of these proteins reported so far, including the possible strategies for their further development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
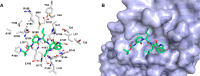
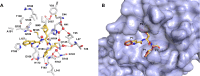
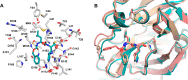
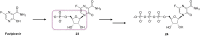
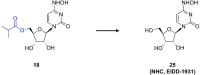
References
-
- Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019; World Health Organization, 2019; https://www.who.int/emergencies/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 (accessed 2020-09-28).
-
- Prioritizing Diseases for Research and Development in Emergency Contexts; World Health Organization, 2020; https://www.who.int/activities/prioritizing-diseases-for-research-and-de... (accessed 2020-09-28).
-
- Wu F.; Zhao S.; Yu B.; Chen Y. M.; Wang W.; Song Z. G.; Hu Y.; Tao Z. W.; Tian J. H.; Pei Y. Y.; Yuan M. L.; Zhang Y. L.; Dai F. H.; Liu Y.; Wang Q. M.; Zheng J. J.; Xu L.; Holmes E. C.; Zhang Y. Z. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Events As They Happen; World Health Organisation, 2019; https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a... (accessed 2020-09-28).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

