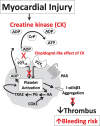
Because of its association with major bleeding the ADP-binding enzyme creatine kinase should be estimated in studies of patients treated for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTE-ACS)
- PMID: 33186454
- PMCID: PMC8203080
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa905
Because of its association with major bleeding the ADP-binding enzyme creatine kinase should be estimated in studies of patients treated for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTE-ACS)
Figures
Comment in
-
Major bleeding and the ADP-binding enzyme creatine kinase in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes.Eur Heart J. 2021 Jun 14;42(23):2313-2314. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa908. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33186455 No abstract available.
Comment on
-
2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation.Eur Heart J. 2021 Apr 7;42(14):1289-1367. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 32860058 No abstract available.
References
-
- Collet J-P, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T, Folliguet T, Gale CP, Gilard M, Jobs A, Jüni P, Lambrinou E, Lewis BS, Mehilli J, Meliga E, Merkely B, Mueller C, Roffi M, Rutten FH, Sibbing D, Siontis GCM, Kastrati A, Mamas MA, Aboyans V, Angiolillo DJ, Bueno H, Bugiardini R, Byrne RA, Castelletti S, Chieffo A, Cornelissen V, Crea F, Delgado V, Drexel H, Gierlotka M, Halvorsen S, Haugaa KH, Jankowska EA, Katus HA, Kinnaird T, Kluin J, Kunadian V, Landmesser U, Leclercq C, Lettino M, Meinila L, Mylotte D, Ndrepepa G, Omerovic E, Pedretti RFE, Petersen SE, Petronio AS, Pontone G, Popescu BA, Potpara T, Ray KK, Luciano F, Richter DJ, Shlyakhto E, Simpson IA, Sousa-Uva M, Storey RF, Touyz RM, Valgimigli M, Vranckx P, Yeh RW, Barbato E, Barthélémy O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T, Folliguet T, Gale CP, Gilard M, Jobs A, Jüni P, Lambrinou E, Lewis BS, Mehilli J, Meliga E, Merkely B, Mueller C, Roffi M, Rutten FH, Sibbing D, Siontis GCM; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2020;doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575.

