Malignant progression of donor-engrafted clonal hematopoiesis in sibling recipients after stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 33186460
- PMCID: PMC7686891
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003168
Malignant progression of donor-engrafted clonal hematopoiesis in sibling recipients after stem cell transplantation
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
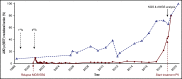

Comment on
-
Clonal hematopoiesis in donors and long-term survivors of related allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Blood. 2020 Apr 30;135(18):1548-1559. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003079. Blood. 2020. PMID: 32181816
References
-
- Boettcher S, Wilk CM, Singer J, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis in donors and long-term survivors of related allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2020;135(18):1548-1559. - PubMed
-
- Van Pelt K, Nollet F, Selleslag D, et al. The JAK2V617F mutation can occur in a hematopoietic stem cell that exhibits no proliferative advantage: a case of human allogeneic transplantation. Blood. 2008;112(3):921-922. - PubMed
-
- Engel N, Rovo A, Badoglio M, et al. ; Transplant Complications Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation . European experience and risk factor analysis of donor cell-derived leukaemias/MDS following haematopoietic cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2019;33(2):508-517. - PubMed

