A Continental Survey on the Impact of COVID-19 on Neurosurgical Training in Africa
- PMID: 33186788
- PMCID: PMC7834456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.11.008
A Continental Survey on the Impact of COVID-19 on Neurosurgical Training in Africa
Abstract
Background: Containment measures for COVID-19 have affected surgical training globally. We sought to assess how neurosurgical training has been affected across Africa in April 2020.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was distributed to African Neurosurgical trainees seeking to review demographics and effects of COVID on training.
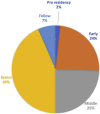
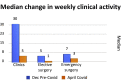
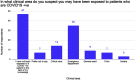
Results: A total of 123 neurosurgery trainees responded from 23 African countries and a further 6 were abroad. A total of 91.80% were men, and 96.70% were training in public institutions. Only 41% had received training in COVID-19 with 61.79% worried that they would contract COVID-19 while performing their clinical duties. There was a marked reduction in clinical activities including a median reduction of elective surgery (-80%), clinics (-83%), and emergency surgery (-38.50%). A total of 23.58% of residents did not receive a formal salary, with 50% on less than $1000 USD gross per month.
Conclusions: This is the first continental survey of neurosurgery trainees in Africa. COVID-19 has significantly affected clinical and learning opportunities. There are concerns of the long-term effects on their training activities for an uncertain period of time during this pandemic. Although there has been a global increase in e-learning, there is need to evaluate if this is accessible to all trainees.
Keywords: Africa; COVID-19; Education; Neurosurgery; Pandemic; Trainees.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)–Africa CDC [Internet] https://africacdc.org/covid-19/ Available at:
-
- Park K.B., Johnson W.D., Dempsey R.J. Global neurosurgery: the unmet need. World Neurosurg. 2016;88:32–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

