Description, prediction and causation: Methodological challenges of studying child and adolescent development
- PMID: 33186867
- PMCID: PMC7670214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2020.100867
Description, prediction and causation: Methodological challenges of studying child and adolescent development
Abstract
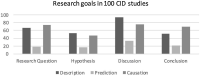
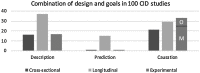
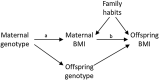
Scientific research can be categorized into: a) descriptive research, with the main goal to summarize characteristics of a group (or person); b) predictive research, with the main goal to forecast future outcomes that can be used for screening, selection, or monitoring; and c) explanatory research, with the main goal to understand the underlying causal mechanism, which can then be used to develop interventions. Since each goal requires different research methods in terms of design, operationalization, model building and evaluation, it should form an important basis for decisions on how to set up and execute a study. To determine the extent to which developmental research is motivated by each goal and how this aligns with the research designs that are used, we evaluated 100 publications from the Consortium on Individual Development (CID). This analysis shows that the match between research goal and research design is not always optimal. We discuss alternative techniques, which are not yet part of the developmental scientist's standard toolbox, but that may help bridge some of the lurking gaps that developmental scientists encounter between their research design and their research goal. These include unsupervised and supervised machine learning, directed acyclical graphs, Mendelian randomization, and target trials.
Keywords: Causality; Developmental science; Directed acyclical graphs; Mendelian randomization; Radical randomization; Target trials.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Allison P.D. SAS Institute; 2006. Fixed Effects Regression Methods for Longitudinal Data Using SAS.
-
- Angrist J.D., Imbens G.W., Rubin D.B. Identification of causal effects using instrumental variables. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996;91:444–455. doi: 10.3386/t0136. - DOI
-
- Angrist J.D., Pischke J.-S. Princeton University Press; Princeton, NJ: 2009. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: an Empiricist’s Companion.
-
- Arlot S., Celisse A. A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection. Statistical Survey. 2010;4:40–79. doi: 10.1214/09-SS054. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

