Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Sintering Pure Titanium and Ti-6Al-4V, and Its Anisotropy
- PMID: 33187166
- PMCID: PMC7696245
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13225081
Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Sintering Pure Titanium and Ti-6Al-4V, and Its Anisotropy
Abstract
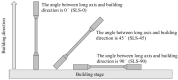
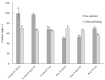
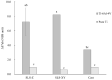
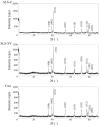
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is being developed for dental applications. This study aimed to investigate the properties of Ti-6Al-4V and pure titanium specimens fabricated using the SLS process and compare them with casting specimens. Besides, the effect of the building direction on the properties of the SLS specimens was also investigated. Specimens were prepared by SLS using Ti-6Al-4V powder or pure titanium powder. Casting specimens were also prepared using Ti-6Al-4V alloys and pure titanium. The mechanical properties (tensile strength and elongation), physical properties (surface roughness, contact angle, and Vickers hardness); corrosion resistors (color difference and corrosion), and surface properties (chemical composition and surface observation) were examined. Both Ti-6Al-4V and pure titanium specimens produced using the SLS process had comparable or superior properties compared with casting specimens. In comparing the building directions, specimens fabricated horizontally to the printing platform showed the greatest tensile strength, and the surface roughness scanned in the horizontal direction to the platform showed the smallest. However, there was no significant effect on other properties. Thus, the SLS process with Ti-6Al-4V powder and pure titanium powder has great performance for the fabrication of dental prosthesis, and there is a possibility for it to take the place of conventional methods.
Keywords: CAD/CAM; Ti-6Al-4V; additive manufacturing; pure titanium; selective laser sintering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



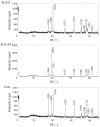
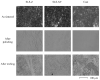
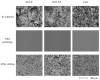
References
-
- Serra-Prat J., Cano-Batalla J., Cabratosa-Termes J., Figueras-Àlvarez O. Adhesion of dental porcelain to cast, milled, and laser-sintered cobalt-chromium alloys: Shear bond strength and sensitivity to thermocycling. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014;112:600–605. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2014.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

