Age differences in the relationships between risk factors and loss of kidney function: a general population cohort study
- PMID: 33187480
- PMCID: PMC7664087
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-020-02121-z
Age differences in the relationships between risk factors and loss of kidney function: a general population cohort study
Abstract
Background: Annual decline in kidney function is a widely applied surrogate outcome of renal failure. It is important to understand the relationships between known risk factors and the annual decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) according to baseline age; however, these remain unclear.
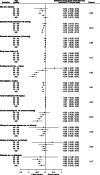
Methods: A community-based retrospective cohort study of adults who underwent annual medical examinations between 1999 and 2013 was conducted. The participants were stratified into different age groups (40-49, 50-59, 60-69, 70-79, and ≥ 80 years) to assess the risk for loss of kidney function. A mixed-effects model was used to estimate the association between risk factors and annual changes in eGFR.
Results: In total, 51,938 participants were included in the analysis. The age group of ≥80 years included 8127 individuals. The mean annual change in eGFR was - 0.39 (95% confidence interval: - 0.41 to - 0.37) mL/min/1.73 m2 per year. Older age was related to faster loss of kidney function. In the older age group, higher systolic blood pressure, proteinuria, and current smoking were related to faster loss of kidney function (p trend < 0.01, 0.03, and < 0.01, respectively). Conversely, each age group showed similar annual loss of kidney function related to lower hemoglobin levels and diabetes mellitus (p trend 0.47 and 0.17, respectively).
Conclusions: Higher systolic blood pressure, proteinuria, and smoking were related to faster loss of kidney function, and a greater effect size was observed in the older participants. More risk assessments for older people are required for personalized care.
Keywords: Aged; Chronic renal insufficiency; Glomerular filtration rate.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dynamic Changes in Renal Function Are Associated With Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2016 Jul;39(7):1259-66. doi: 10.2337/dc15-2607. Epub 2016 May 23. Diabetes Care. 2016. PMID: 27222502
-
Sex Differences in the Progression of CKD Among Older Patients: Pooled Analysis of 4 Cohort Studies.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Jan;75(1):30-38. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.05.019. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 31409508
-
Risk of Progression of Nonalbuminuric CKD to End-Stage Kidney Disease in People With Diabetes: The CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Nov;72(5):653-661. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.02.364. Epub 2018 May 18. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29784612
-
High Ambulatory Arterial Stiffness Index Is an Independent Risk Factor for Rapid Age-Related Glomerular Filtration Rate Decline in the General Middle-Aged Population.Hypertension. 2017 Apr;69(4):651-659. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09020. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28223468
-
Subclinical Kidney Damage in Hypertensive Patients: A Renal Window Opened on the Cardiovascular System. Focus on Microalbuminuria.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:279-306. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_85. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873229 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictors of decline in kidney function in the general population: a decade of follow-up from the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):2216020. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2216020. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37272290 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Quality of Life Between Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis and Hemodialysis in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Feb 1;17(2):e78328. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78328. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40034626 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the epidemiology, management and outcomes of kidney disease in men and women.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Jan;20(1):7-20. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00784-z. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37985869 Review.
-
Trends in renal function in Northern Sweden 1986-2014: data from the seven cross-sectional surveys within the Northern Sweden MONICA study.BMJ Open. 2023 Aug 30;13(8):e072664. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072664. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37648389 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Outcomes in Patients with CKD and Rapid or Non-rapid eGFR Decline: A Report from the DISCOVER CKD Retrospective Cohort.Adv Ther. 2024 Aug;41(8):3264-3277. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02913-x. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38958839 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

