Optimizing Disclosure of HIV Status to a Diverse Population of HIV-Positive Youth at an Urban Pediatric HIV Clinic
- PMID: 33187819
- PMCID: PMC10233458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.10.010
Optimizing Disclosure of HIV Status to a Diverse Population of HIV-Positive Youth at an Urban Pediatric HIV Clinic
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of the study was to increase the proportion of youth living with HIV (YLWH) aged ≥11 years who undergo developmentally appropriate disclosure about their HIV status.
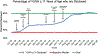
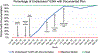
Methods: A quality improvement project was initiated at an urban pediatric HIV clinic between July 2018 and March 2020. The primary outcome measure was the proportion of YLWH aged ≥11 years who were disclosed to about their HIV status. The proportion of undisclosed YLWH who had documented nondisclosure status was also assessed as a process measure. Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles for change included monthly clinic staff check-ins to discuss new disclosures, quarterly team meetings to discuss strategies to improve disclosure, and modifying a clinic note template to prompt providers to document disclosure status. Annotated run charts were used to analyze the data.
Results: Before the first PDSA cycle, 26/46 (57%) of the target population of YLWH aged ≥11 years had their HIV status disclosed to them, and none of the undisclosed youth had disclosure status documented in their medical record. After 20 months and six PDSA cycles, the proportion of YLWH aged ≥11 years disclosed to about their HIV status increased to 80% and the proportion of undisclosed YLWH with documentation of their disclosure status increased to 100%.
Conclusions: Several interventions integrated throughout the pediatric HIV care process were associated with an increase in the proportion of YLWH with developmentally appropriate HIV disclosure and documentation of disclosure status, an important psychosocial aspect of care in these individuals.
Keywords: Adolescent health; Disclosure; HIV; Quality improvement.
Copyright © 2020 Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Disclosure of HIV Status to Youth With Perinatally-Acquired HIV: The Dilemma, Risks, and Responsibilities.J Adolesc Health. 2021 Apr;68(4):639-641. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.01.007. J Adolesc Health. 2021. PMID: 33781468 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hazra R, Siberry GK, Mofenson LM. Growing up with HIV: Children, adolescents, and young adults with perinatally acquired HIV infection. Annu Rev Med 2010;61:169–85. - PubMed
-
- CDC. HIV surveillance report, 2018. (preliminary). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveil.... Accessed March 13, 2020.
-
- Sabharwal S, Mitchell JW, Fan VY. Should there be a disclosure mandate for physicians caring for perinatally infected adolescents who don’t know their HIV serostatus? AMA J Ethics 2018;20:E743–9. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Guideline on HIV disclosure counseling for children up to 12 years of age HIV/AIDS programme. 2011. Available at: https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/hiv_disclosure/en/. Accessed November 4, 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

