Multiscale dynamics of colloidal deposition and erosion in porous media
- PMID: 33188022
- PMCID: PMC7673751
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc2530
Multiscale dynamics of colloidal deposition and erosion in porous media
Abstract
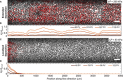
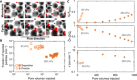
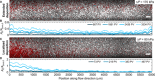
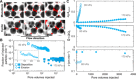
Diverse processes-e.g., environmental pollution, groundwater remediation, oil recovery, filtration, and drug delivery-involve the transport of colloidal particles in porous media. Using confocal microscopy, we directly visualize this process in situ and thereby identify the fundamental mechanisms by which particles are distributed throughout a medium. At high injection pressures, hydrodynamic stresses cause particles to be continually deposited on and eroded from the solid matrix-notably, forcing them to be distributed throughout the entire medium. By contrast, at low injection pressures, the relative influence of erosion is suppressed, causing particles to localize near the inlet of the medium. Unexpectedly, these macroscopic distribution behaviors depend on imposed pressure in similar ways for particles of different charges, although the pore-scale distribution of deposition is sensitive to particle charge. These results reveal how the multiscale interactions between fluid, particles, and the solid matrix control how colloids are distributed in a porous medium.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

References
-
- Phenrat T., Kim H.-J., Fagerlund F., Illangasekare T., Tilton R. D., Lowry G. V., Particle size distribution, concentration, and magnetic attraction affect transport of polymer-modified Fe0 nanoparticles in sand columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 5079–5085 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Zhao X., Liu W., Cai Z., Han B., Qian T., Zhao D., An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation. Water Res. 100, 245–266 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Kanel S. R., Grenèche J.-M., Choi H., Arsenic(V) removal from groundwater using nano scale zero-valent iron as a colloidal reactive barrier material. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 2045–2050 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Zhang H., Nikolov A., Wasan D., Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) using nanoparticle dispersions: Underlying mechanism and imbibition experiments. Energy Fuel 28, 3002–3009 (2014).
-
- Tang R., Kim C. S., Solfiell D. J., Rana S., Mout R., Velázquez-Delgado E. M., Chompoosor A., Jeong Y., Yan B., Zhu Z.-J., Kim C., Hardy J. A., Rotello V. M., Direct delivery of functional proteins and enzymes to the cytosol using nanoparticle-stabilized nanocapsules. ACS Nano 7, 6667–6673 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

