Room temperature 3D printing of super-soft and solvent-free elastomers
- PMID: 33188029
- PMCID: PMC7673745
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc6900
Room temperature 3D printing of super-soft and solvent-free elastomers
Abstract
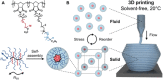
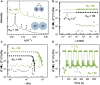
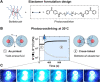
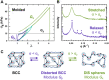
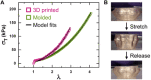
Super-soft elastomers derived from bottlebrush polymers show promise as advanced materials for biomimetic tissue and device applications, but current processing strategies are restricted to simple molding. Here, we introduce a design concept that enables the three-dimensional (3D) printing of super-soft and solvent-free bottlebrush elastomers at room temperature. The key advance is a class of inks comprising statistical bottlebrush polymers that self-assemble into well-ordered body-centered cubic sphere phases. These soft solids undergo sharp and reversible yielding at 20°C in response to shear with a yield stress that can be tuned by manipulating the length scale of microphase separation. The addition of a soluble photocrosslinker allows complete ultraviolet curing after extrusion to form super-soft elastomers with near-perfect recoverable elasticity well beyond the yield strain. These structure-property design rules create exciting opportunities to tailor the performance of 3D-printed elastomers in ways that are not possible with current materials and processes.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

References
-
- Verduzco R., Li X., Pesek S. L., Stein G. E., Structure, function, self-assembly, and applications of bottlebrush copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 2405–2420 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Rzayev J., Molecular bottlebrushes: New opportunities in nanomaterials fabrication. ACS Macro Lett. 1, 1146–1149 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Sheiko S. S., Dobrynin A. V., Architectural code for rubber elasticity: From supersoft to superfirm materials. Macromolecules 52, 7581–7546 (2019).
-
- Daniel W. F. M., Burdyńska J., Vatankhah-Varnoosfaderani M., Matyjaszewski K., Paturej J., Rubinstein M., Dobrynin A. V., Sheiko S. S., Solvent-free, supersoft and superelastic bottlebrush melts and networks. Nat. Mater. 15, 183–189 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani M., Daniel W. F. M., Everhart M. H., Pandya A. A., Liang H., Matyjaszewski K., Dobrynin A. V., Sheiko S. S., Mimicking biological stress–strain behaviour with synthetic elastomers. Nature 549, 497–501 (2017). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

