From particle attachment to space-filling coral skeletons
- PMID: 33188087
- PMCID: PMC7720159
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2012025117
From particle attachment to space-filling coral skeletons
Abstract
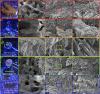
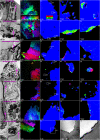
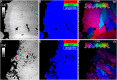
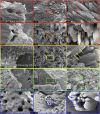
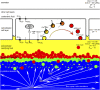
Reef-building corals and their aragonite (CaCO3) skeletons support entire reef ecosystems, yet their formation mechanism is poorly understood. Here we used synchrotron spectromicroscopy to observe the nanoscale mineralogy of fresh, forming skeletons from six species spanning all reef-forming coral morphologies: Branching, encrusting, massive, and table. In all species, hydrated and anhydrous amorphous calcium carbonate nanoparticles were precursors for skeletal growth, as previously observed in a single species. The amorphous precursors here were observed in tissue, between tissue and skeleton, and at growth fronts of the skeleton, within a low-density nano- or microporous layer varying in thickness from 7 to 20 µm. Brunauer-Emmett-Teller measurements, however, indicated that the mature skeletons at the microscale were space-filling, comparable to single crystals of geologic aragonite. Nanoparticles alone can never fill space completely, thus ion-by-ion filling must be invoked to fill interstitial pores. Such ion-by-ion diffusion and attachment may occur from the supersaturated calcifying fluid known to exist in corals, or from a dense liquid precursor, observed in synthetic systems but never in biogenic ones. Concomitant particle attachment and ion-by-ion filling was previously observed in synthetic calcite rhombohedra, but never in aragonite pseudohexagonal prisms, synthetic or biogenic, as observed here. Models for biomineral growth, isotope incorporation, and coral skeletons' resilience to ocean warming and acidification must take into account the dual formation mechanism, including particle attachment and ion-by-ion space filling.
Keywords: PEEM; aragonite; biomineral; coral skeleton formation; spectromicroscopy.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hoegh-Guldberg O., et al. , Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 318, 1737–1742 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pandolfi J. M., Connolly S. R., Marshall D. J., Cohen A. L., Projecting coral reef futures under global warming and ocean acidification. Science 333, 418–422 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Hughes T. P., et al. , Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 543, 373–377 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Carpenter K. E., et al. , One-third of reef-building corals face elevated extinction risk from climate change and local impacts. Science 321, 560–563 (2008). - PubMed

