The relationship between intraoperative cerebral oximetry and postoperative delirium in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a retrospective study
- PMID: 33189145
- PMCID: PMC7666484
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-020-01180-x
The relationship between intraoperative cerebral oximetry and postoperative delirium in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Cerebral oximetry has been widely used to measure regional oxygen saturation in brain tissue, especially during cardiac surgery. Despite its popularity, there have been inconsistent results on the use of cerebral oximetry during cardiac surgery, and few studies have evaluated cerebral oximetry during off pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery (OPCAB).
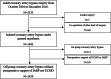
Methods: To evaluate the relationship between intraoperative cerebral oximetry and postoperative delirium in patients who underwent OPCAB, we included 1439 patients who underwent OPCAB between October 2004 and December 2016 and among them, 815 patients with sufficient data on regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2) were enrolled in this study. We retrospectively analyzed perioperative variables and the reduction in rSO2 below cut-off values of 75, 70, 65, 60, 55, 50, 45, 40, and 35%. Furthermore, we evaluated the relationship between the reduction in rSO2 and postoperative delirium.
Results: Delirium occurred in 105 of 815 patients. In both univariable and multivariable analyses, the duration of rSO2 reduction was significantly longer in patients with delirium at cut-offs of < 50 and 45% (for every 5 min, adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.007 [95% Confidence interval (CI) 1.001 to 1.014] and adjusted OR 1.012 [1.003 to 1.021]; p = 0.024 and 0.011, respectively). The proportion of patients with a rSO2 reduction < 45% was significantly higher among those with delirium (adjusted OR 1.737[1.064 to 2.836], p = 0.027).
Conclusions: In patients undergoing OPCAB, intraoperative rSO2 reduction was associated with postoperative delirium. Duration of rSO2 less than 50% was 40% longer in the patients with postoperative delirium. The cut-off value of intraoperative rSO2 that associated with postoperative delirium was 50% for the total patient population and 55% for the patients younger than 68 years.
Keywords: Cerebral oximetry; Delirium; Off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Effect of percutaneous cerebral oximetry-guided anaesthetic management on postoperative delirium in older adults undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: study protocol for a single-centre prospective randomised controlled trial in a tertiary academic hospital in China.BMJ Open. 2023 Dec 9;13(12):e076419. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076419. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 38070897 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative Near Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements of Cerebral Regional Oxygen Desaturations Are Not Associated With Delirium After Cardiac Surgery.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2025 May;39(5):1153-1161. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2025.01.034. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40000288
-
Influence of intraoperative cerebral oximetry monitoring on neurocognitive function after coronary artery bypass surgery: a randomized, prospective study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015 Mar;47(3):447-54. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezu193. Epub 2014 May 7. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 24810757 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of electroencephalography and regional cerebral oxygen saturation monitoring on perioperative neurocognitive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 Sep 30;20(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01163-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32998697 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Intraoperative Cerebral Oximetry Monitoring on Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction and ICU Stay in Adult Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 1;8:814313. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.814313. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35178431 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Behavioural and physiological responses to stressors in sheep with temperament classified by genotype or phenotype.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 8;14(1):8147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58959-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38584170 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of percutaneous cerebral oximetry-guided anaesthetic management on postoperative delirium in older adults undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: study protocol for a single-centre prospective randomised controlled trial in a tertiary academic hospital in China.BMJ Open. 2023 Dec 9;13(12):e076419. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076419. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 38070897 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of Concurrent Cerebral Desaturation and Electroencephalographic Burst Suppression in Cardiac Surgery Patients.Anesth Analg. 2025 May 1;140(5):1086-1092. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000007209. Anesth Analg. 2025. PMID: 39446661
-
Perioperative neurocognitive disorders: A narrative review focusing on diagnosis, prevention, and treatment.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Aug;28(8):1147-1167. doi: 10.1111/cns.13873. Epub 2022 Jun 1. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35652170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of rScO2-Guided Blood Pressure Management on Postoperative Complications in Elderly Patients After Major Noncardiac Surgery: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Aug 25;16:3789-3796. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S426245. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37649853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tosh W, Patteril M. Cerebral oximetry. BJA Educ. 2016;16(12):417–421. doi: 10.1093/bjaed/mkw024. - DOI
-
- Payabvash S, Souza LC, Wang Y, Schaefer PW, Furie KL, Halpern EF, et al. Regional ischemic vulnerability of the brain to hypoperfusion: the need for location specific computed tomography perfusion thresholds in acute stroke patients. Stroke. 2011;42(5):1255–1260. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.600940. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources