Effectiveness and safety of intravenous tocilizumab to treat COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: Covizumab-6 observational cohort
- PMID: 33189888
- PMCID: PMC7658611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108631
Effectiveness and safety of intravenous tocilizumab to treat COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: Covizumab-6 observational cohort
Abstract
Although the starting event in COVID-19 is a viral infection some patients present with an over-exuberant inflammatory response, leading to acute lung injury (ALI) and adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Since IL-6 plays a critical role in the inflammatory response, we assessed the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab (TCZ) in this single-centre, observational study in all Covid-19 in-patient with a proven SARS-CoV-2 rapidly progressing infection to prevent ALI and ARDS. 104 patients with COVID-19 treated with TCZ had a lower mortality rate (5·8%) compared with the regional mortality rate (11%), hospitalized patient's mortality (10%), and slightly lower than hospitalized patients treated with our standard of care alone (6%). We found that TCZ rapidly decreased acute phase reactants, ferritin and liver release of proteins. D-Dimer decreased slowly. We did not observe specific safety concerns. Early administration of IL6-R antagonists in COVID-19 patients with impending hyperinflammatory response, may be safe and effective treatment to prevent, ICU admission and further complications.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine release syndrome; IL-6R antagonist; SARS-CoV-2; Tocilizumab; Treatment.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The study received no funding. The authors declare no conflict of interest for this manuscript.
All researchers played a role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Figures

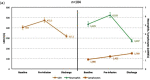

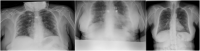
Comment in
-
Commensal bacterial metabolites may strengthen the effect of anti-IL6 treatment for COVID-19.Clin Immunol. 2021 Nov;232:108870. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2021.108870. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34601117 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G. Discovery of a novel coronavirus associated with the recent pneumonia outbreak in humans and its potential bat origin. bioRxiv. 2020;20
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

