Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 infection: a systematic review
- PMID: 33190794
- PMCID: PMC7582054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.017
Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 infection: a systematic review
Abstract
Objectives: Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a major cause of hospital admission and represents a challenge for patient management during intensive care unit (ICU) stay. We aimed to describe the clinical course and outcomes of COVID-19 pneumonia in critically ill patients.
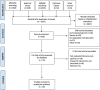
Methods: We performed a systematic search of peer-reviewed publications in MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library up to 15th August 2020. Preprints and reports were also included if they met the inclusion criteria. Study eligibility criteria were full-text prospective, retrospective or registry-based publications describing outcomes in patients admitted to the ICU for COVID-19, using a validated test. Participants were critically ill patients admitted in the ICU with COVID-19 infection.
Results: From 32 articles included, a total of 69 093 patients were admitted to the ICU and were evaluated. Most patients included in the studies were male (76 165/128 168, 59%, 26 studies) and the mean patient age was 56 (95%CI 48.5-59.8) years. Studies described high ICU mortality (21 145/65 383, 32.3%, 15 studies). The median length of ICU stay was 9.0 (95%CI 6.5-11.2) days, described in five studies. More than half the patients admitted to the ICU required mechanical ventilation (31 213/53 465, 58%, 23 studies) and among them mortality was very high (27 972/47 632, 59%, six studies). The duration of mechanical ventilation was 8.4 (95%CI 1.6-13.7) days. The main interventions described were the use of non-invasive ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, renal replacement therapy and vasopressors.
Conclusions: This systematic review, including approximately 69 000 ICU patients, demonstrates that COVID-19 infection in critically ill patients is associated with great need for life-sustaining interventions, high mortality, and prolonged length of ICU stay.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critically ill; ICU; Outcomes; Resource; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: 'Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 infection: a systematic review' by Serafim et al.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Jun;27(6):938-939. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.010. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33484842 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): situation report 111. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed July 23 2020.
-
- ISARIC (International Severe Acute Respiratory and emerging Infection Consorti Database) 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous