Effects of HuoxueJiangtang decoction alone or in combination with metformin on renal function and renal cortical mRNA expression in diabetic nephropathy rats
- PMID: 33191822
- PMCID: PMC7671697
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1844242
Effects of HuoxueJiangtang decoction alone or in combination with metformin on renal function and renal cortical mRNA expression in diabetic nephropathy rats
Abstract
Context: HuoxueJiangtang decoction (ZY) is a traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of diabetes.
Objective: The protective effect of ZY on renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats was investigated in this study.
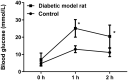
Materials and methods: Fifty 4-week-old SPF Wistar male rats were selected to construct diabetic nephropathy model rats (DN) group by continuous high-fat feeding for 4 weeks, followed by a tail vein injection of 30 mg/kg streptozotocin for 1 week. The experimental rats were divided into six groups of 10 rats: normal (control), DN, DN + ZY, DN + metformin, DN + metformin + ZY, and DN + metformin + captopril (positive control) groups. Among the groups, 6.25 g/kg ZY, 250 mg/kg metformin, and 17.5 mg/kg captopril were given to the rats by gavage once a day for 16 weeks. Blood glucose, dietary behaviour, biochemical indicators, and gene expression changes were measured in each group.
Results: Metformin + ZY treatment significantly lowered blood glucose, water intake, urine total protein, urine albumin, urine volume, serum triglyceride, and serum cholesterol levels in the DN group. The pathological changes of kidney tissue showed that the DN + metformin + ZY group had a protective effect on kidney tissue damage. And ZY and metformin + ZY treatments repaired the expression of genes in the DN group.
Discussion and conclusion: The ZY and metformin combined treatment showed a clear therapeutic effect on kidney damage in DN. This study provides a potential mechanism for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy with ZY combined with metformin.
Keywords: Blood glucose; biochemical indicator; kidney; pathological change.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Alhaider AA, Korashy HM, Sayed-Ahmed MM, Mobark M, Kfoury H, Mansour MA.. 2011. Metformin attenuates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats through modulation of oxidative stress genes expression. Chem Biol Interact. 192(3):233–242. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. 2014. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 37(Suppl 1):S81–S90. - PubMed
-
- Arcaro CA, Assis RP, Zanon NM, Paula-Gomes S, Navegantes LCC, Kettelhut IC, Brunetti IL, Baviera AM.. 2018. Involvement of cAMP/EPAC/Akt signaling in the antiproteolytic effects of pentoxifylline on skeletal muscles of diabetic rats. J Appl Physiol. 124(3):704–716. - PubMed
-
- Basta-Jovanovic G, Venkataseshan VS, Gil J, Kim DU, Dikman SH, Churg J.. 1990. Morphometric analysis of glomerular basement membranes (GBM) in thin basement membrane disease (TBMD). Clin Nephrol. 33(3):110–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
