Total hip arthroplasty in acetabular fractures
- PMID: 33192013
- PMCID: PMC7656485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.10.037
Total hip arthroplasty in acetabular fractures
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021 Aug 5;21:101558. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101558. eCollection 2021 Oct. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021. PMID: 34414072 Free PMC article.
Abstract
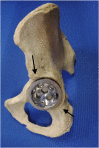
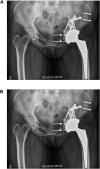
Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) is a well-accepted treatment for established hip arthritis following acetabular fractures. If a conservatively managed or operated case progresses to non-union/mal-union failing to restore the joint integrity, it may eventually develop secondary arthritis warranting a total hip arthroplasty. Also, in recent years, acute total hip arthroplasty is gaining importance in conditions where the fracture presents with pre-existing hip arthritis, is not amenable to salvage by open reduction and internal fixation, or, a poor prognosis is anticipated following fixation. There are several surgical challenges in performing total hip arthroplasty for acetabular fractures whether acute or delayed. As a separate entity elderly patients pose a distinct challenge due to osteoporosis and need stable fixation for early weight bearing alleviating the risk of any thromboembolic event, pulmonary complications and decubitus ulcer. The aim of surgery is to restore the columns for acetabular component implantation rather than anatomic fixation. Meticulous preoperative planning with radiographs and Computed Tomography (CT) scans, adequate exposure to delineate the fracture pattern, and, availability of an array of all instruments and possible implants as backup are the key points for success. Previous implants if any should be removed only if they are in the way of cup implantation or infected. Press fit uncemented modern porous metal acetabular component with multiple screw options is the preferred implant for majority of cases. However, complex fractures may require major reconstruction with revision THA implants especially when a pelvic discontinuity is present.
Keywords: Acetabular fracture; Pelvic discontinuity; Post traumatic osteoarthritis; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2020 Delhi Orthopedic Association. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ferguson T.A., Patel R., BhandariM Matta JM. Fractures of the acetabulum in patients aged 60 years and older: an epidemiological and radiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(2):250–257. - PubMed
-
- Giannoudis P.V., Grotz M.R.W., Papakostidis C. Operative treatment of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87B:1–9. - PubMed
-
- O’Toole R.V., Hui E., Chandra A., Nascone J.W. How often does open reduction and internal fixation of geriatric acetabular fractures lead to hip arthroplasty? J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(3):148–153. - PubMed
-
- Mears D.C., Velyvis J.H. Acute total hip arthroplasty for selected displaced acetabular fractures. 2- 12 year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(1) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

