Local Delivery of Minocycline and Vorinostat Targets the Tumor Microenvironment to Inhibit the Recurrence of Glioma
- PMID: 33192073
- PMCID: PMC7655508
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S273527
Local Delivery of Minocycline and Vorinostat Targets the Tumor Microenvironment to Inhibit the Recurrence of Glioma
Abstract
Background: Postoperative recurrence is the main reason for poor clinical outcomes in glioma patients, so preventing tumor recurrence is crucial in the management of gliomas.
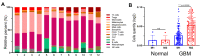
Methods: In this study, the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in normal tissues was detected via RNA-seq analysis. Glioma cases from the public databases (The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA)) were included in this study. The hydrogel contains minocycline (Mino) and vorinostat (Vor) (G/Mino+Vor) was formed under 365 nm when the photoinitiator was added. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to assess the release of drugs in the G/Mino+Vor hydrogel. An MTT assay was used to explore the biosecurity of GelMA. Immunohistochemistry, ELISA, and TUNEL assays were used to demonstrate the antitumor effect of the G/Mino+Vor hydrogel.
Results: We successfully developed a G/Mino+Vor hydrogel. The experiments in vitro and in vivo confirmed the MMPs-responsive delivery of minocycline and vorinostat in hydrogel and the anti-glioma effect on an incomplete tumor operation model, which indicated that the G/Mino+Vor hydrogel effectively inhibited the recurrence of glioma after surgery.
Conclusion: In summary, the G/Mino+Vor hydrogel could continuously release drugs and improve the therapy effects against recurrent glioma.
Keywords: hydrogel; minocycline; recurrent glioma; tumor microenvironmennt; vorinostat.
© 2020 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Meyer MA. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(17):1850; author reply 1850. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. European organisation for, R.; treatment of cancer brain, T.; radiotherapy, G.; national cancer institute of canada clinical trials, G., radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

