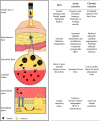
Factors Influencing Insulin Absorption Around Exercise in Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 33193089
- PMCID: PMC7609903
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.573275
Factors Influencing Insulin Absorption Around Exercise in Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
International charities and health care organizations advocate regular physical activity for health benefit in people with type 1 diabetes. Clinical expert and international diabetes organizations' position statements support the management of good glycemia during acute physical exercise by adjusting exogenous insulin and/or carbohydrate intake. Yet research has detailed, and patients frequently report, variable blood glucose responses following both the same physical exercise session and insulin to carbohydrate alteration. One important source of this variability is insulin delivery to the circulation. With modern insulin analogs, it is important to understand how different insulins, their delivery methods, and inherent physiological factors, influence the reproducibility of insulin absorption from the injection site into circulation. Furthermore, contrary to the adaptive pancreatic response to exercise in the person without diabetes, the physiological and metabolic shifts with exercise may increase circulating insulin concentrations that may contribute to exercise-related hyperinsulinemia and consequent hypoglycemia. Thus, a furthered understanding of factors underpinning insulin delivery may offer more confidence for healthcare professionals and patients when looking to improve management of glycemia around exercise.
Keywords: absorption; exercise; insulin; pharmacokinetics; physiology; subcutaneous tissue; type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Copyright © 2020 Pitt, McCarthy, Hoeg-Jensen, Wellman and Bracken.
Figures