Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates inflammation in a rat model of myocardial infarction via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 33193843
- PMCID: PMC7646702
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9368
Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates inflammation in a rat model of myocardial infarction via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
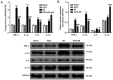
Inflammation serves an important role in myocardial infarction (MI). Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3), an activator of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), has been identified to elicit anti-inflammatory effects via the NF-κB pathway. However, the function of Rg3 in MI remains unknown. In the present study, a MI rat model was established by coronary artery ligation and treated with Rg3 to explore whether Rg3 could inhibit inflammation in MI rats by inhibiting the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. At 28 days post-MI, it was identified that Rg3 not only decreased the ST-segment ECG values in MI rats, but also significantly decreased serum LDH, CK-MB and cTnI levels in MI rats. In addition, Rg3 also significantly decreased serum tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 levels and increased serum IL-10 levels in MI rats. In the heart tissues of the MI rats, Rg3 attenuated myocardial pathological changes and cell apoptosis caused by MI, decreased the gene expression levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, but increased the gene expression level of IL-10. In addition, the expression levels of the SIRT1 and transcription factor RelB proteins were significantly increased following Rg3 treatment, and the expression level of p-p65/p65 protein was significantly decreased in the heart tissues of MI rats with Rg3 treatment compared with that in heart tissues of MI rats without Rg3 treatment. In conclusion, Rg3 alleviates inflammation in a rat model of MI via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: ginsenoside Rg3; inflammation; myocardial infarction; sirtuin 1/NF-κB.
Copyright: © Tu et al.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
