Development of 3D bioprinting: From printing methods to biomedical applications
- PMID: 33193859
- PMCID: PMC7610207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2019.11.003
Development of 3D bioprinting: From printing methods to biomedical applications
Abstract
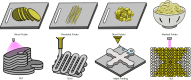
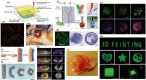
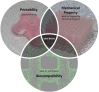
Biomanufacturing of tissues/organs in vitro is our big dream, driven by two needs: organ transplantation and accurate tissue models. Over the last decades, 3D bioprinting has been widely applied in the construction of many tissues/organs such as skins, vessels, hearts, etc., which can not only lay a foundation for the grand goal of organ replacement, but also be served as in vitro models committed to pharmacokinetics, drug screening and so on. As organs are so complicated, many bioprinting methods are exploited to figure out the challenges of different applications. So the question is how to choose the suitable bioprinting method? Herein, we systematically review the evolution, process and classification of 3D bioprinting with an emphasis on the fundamental printing principles and commercialized bioprinters. We summarize and classify extrusion-based, droplet-based, and photocuring-based bioprinting methods and give some advices for applications. Among them, coaxial and multi-material bioprinting are highlighted and basic principles of designing bioinks are also discussed.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; Bioink; Droplet-based bioprinting; Extrusion-based bioprinting; Photocuring-based bioprinting.
© 2019 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures















References
-
- He Y., Gao Q., Liu A., Sun M., Fu J. 3D bioprinting: from structure to function. J Zhejiang Univ (Eng Sci) 2019;53(3):1–12.
-
- Dong H., Fang Y., Wang D., Zhang H., Lei L., Luo Y. Current situation and thinking of organ donation at home and abroad. J Nurs. 2017;24(11):23–26.
-
- Mironov V., Boland T., Trusk T., Forgacs G., Markwald R.R. Organ printing: computer-aided jet-based 3D tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2003;21(4):157–161. - PubMed
-
- Boland T., Mironov V., Gutowska A., Roth E.A., Markwald R.R. Cell and organ printing 2: fusion of cell aggregates in three‐dimensional gels. Anat Rec Part A. 2003;272(2):497–502. - PubMed
-
- Mironov V. Printing technology to produce living tissue. Exp Opin Biol Ther. 2003;3(5):701–704. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

