The role of Transfer RNA-Derived Small RNAs (tsRNAs) in Digestive System Tumors
- PMID: 33193887
- PMCID: PMC7646161
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.46055
The role of Transfer RNA-Derived Small RNAs (tsRNAs) in Digestive System Tumors
Abstract
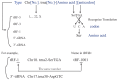
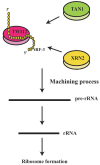
Transfer RNA-derived small RNA(tsRNA) is a type of non-coding tRNA undergoing cleavage by specific nucleases such as Dicer. TsRNAs comprise of tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) and tRNA halves (tiRNAs). Based on the splicing site within the tRNA, tRFs can be classified into tRF-1, tRF-2, tRF-3, tRF-5, and i-tRF. TiRNAs can be classified into 5'-tiRNA and 3'-tiRNA. Both tRFs and tiRNAs have important roles in carcinogenesis, especially cancer of digestive system. TRFs and tiRNAs can promote cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by regulating the expression of oncogenes, combining with RNA binding proteins such as Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1) to prevent transcription. Despite many reviews on the basic biological function of tRFs and tiRNAs, few have described their correlation with tumors especially gastrointestinal tumor. This review focused on the relationship of tRFs and tiRNAs with the biological behavior, clinicopathological characteristics, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of digestive system tumors, and would provide novel insights for the early detection and treatment of digestive system tumors.
Keywords: cancer; digestive system tumors; tRFs; tRNAs; tiRNAs; tsRNAs.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
tRNA-derived fragments and tRNA halves: The new players in cancers.Cancer Lett. 2019 Jun 28;452:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30905816
-
The Emerging Function and Promise of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Cancer.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 27;15(6):1642-1656. doi: 10.7150/jca.89219. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38370372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression Profiles and Function Predictions for tRFs & tiRNAs in Skin Injury Induced by Ultraviolet Irradiation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 10;9:707572. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.707572. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34447751 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and potential role of tRFs and tiRNAs derived from tRNAs in the carcinogenesis and development of lung adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jul;22(1):506. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12767. Epub 2021 May 2. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33986867 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer RNA-derived fragments and tRNA halves: biogenesis, biological functions and their roles in diseases.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Nov;96(11):1167-1176. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1693-y. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30232504 Review.
Cited by
-
5'-tRF-19-Q1Q89PJZ Suppresses the Proliferation and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via Regulating Hexokinase 1-Mediated Glycolysis.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 12;13(10):1513. doi: 10.3390/biom13101513. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892195 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA-derived fragments in gastric cancer: Biomarkers and functions.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Sep;26(18):4768-4780. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17511. Epub 2022 Aug 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35957621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification, function, and advances in tsRNA in non-neoplastic diseases.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Nov 16;14(11):748. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06250-9. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37973899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-31-79MP9P9NH57SD acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jul;36(7):10.1002/jcla.24492. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24492. Epub 2022 May 16. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35576497 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous tRNA-derived small RNA (tRF3-Thr-AGT) inhibits ZBP1/NLRP3 pathway-mediated cell pyroptosis to attenuate acute pancreatitis (AP).J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(22):10441-10453. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16972. Epub 2021 Oct 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34643045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang B, Yang H, Cheng X, Wang D, Fu S, Shen W. et al. tRF/miR-1280 Suppresses Stem Cell-like Cells and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77(12):3194–206. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

