Sodium to globulin ratio as a prognostic factor for patients with advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 33193896
- PMCID: PMC7646180
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.47314
Sodium to globulin ratio as a prognostic factor for patients with advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
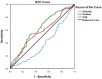
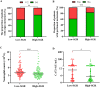
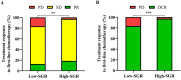
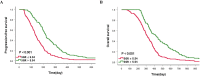
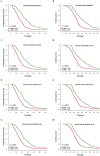
Background: Electrolyte disturbance and systemic inflammation contributes to poor prognosis of cancer patients. Levels of serum sodium and globulin can reflect electrolyte homeostasis and inflammatory state, respectively, therefore have potential as prognostic factors for cancer patients. In this study, we hypothesized that sodium to globulin ratio (SGR) could have superior accuracy in predicting cancer patient survival, than sodium and globulin alone. We therefore sought to investigate its efficacy in prognosis of patients with advanced gastric cancer (GC) receiving first-line chemotherapy. Methods: A total of 265 patients, with advanced GC, were recruited in this retrospective study from January 2014 to January 2019. We first determined SGR cut-off values using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, then analyzed the relationship between pretreatment SGR and clinicopathological features and the effect of chemotherapy. Finally, we evaluated progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates of the entire and subgroup populations using univariate and multivariate logistic regressions. Results: SGR recorded a cut-off value of 5.54, and had a significantly higher area under the curve (AUC) value (0.619, p = 0.001) than fibrinogen (0.575, p = 0.034) and albumin (0.610, p = 0.002) alone. Organ metastasis, and peritoneal invasion ratios, as well as neutrophil and CA72-4 levels varied significantly between the low-SGR (SGR≤ 5.54) and high SGR (SGR> 5.54) groups (all p < 0.05). Specifically, patients in the low-SGR group exhibited significantly lower disease control rates (83.4%) than those in the high-SGR group (97.2%) (p < 0.001). Results from multivariate analysis indicated that high-SGR was an independent risk factor for PFS (Hazard ratio [HR]: 0.539, p < 0.001) and OS (HR: 0.574, p < 0.001). Moreover, patients in the low-SGR group exhibited significantly worse PFS (134 vs. 221 days, p < 0.001) and OS (311 vs. 420 days, p < 0.001) than those in the high-SGR group. Furthermore, subgroup analysis revealed that SGR was still a powerful prognostic indicator in GC patients with good prognosis or normal biochemical indexes, including no peritoneal infiltration, normal neutrophil counts, and normal serum sodium and globulin levels (all p < 0.001). Conclusions: Overall, our findings indicate that SGR is a novel and promising prognostic factor for GC patients. It has superior accuracy, to sodium and globulin alone, hence it is a powerful tool for evaluating effects of treatment, PFS, and OS in patients with advanced GC, who receive first-line chemotherapy.
Keywords: first-line chemotherapy; gastric cancer; overall survival; prognosis; progression-free survival; sodium to globulin ratio.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A. et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 2010;376:687–97. - PubMed
-
- Rosner MH, Dalkin AC. Electrolyte disorders associated with cancer. Advances in chronic kidney disease. 2014;21:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet (London, England) 2001;357:539–45. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

