Oral Administration of Quercetin or Its Derivatives Inhibit Bone Loss in Animal Model of Osteoporosis
- PMID: 33194005
- PMCID: PMC7641676
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6080597
Oral Administration of Quercetin or Its Derivatives Inhibit Bone Loss in Animal Model of Osteoporosis
Abstract
Objectives. Quercetin (Q) and its derivatives are the major members of the naturally occurring flavonoid family, which possess beneficial effects on disease prevention including osteoporosis. The present study is aimed at further investigating the efficacy of the Q and its derivatives on bone pathology, bone-related parameters under imageology, bone maximum load, and serum bone metabolism indexes in animal model of osteoporosis. Potential mechanisms of Q and its derivatives in the treatment of osteoporosis as well as the existing problems regarding the modeling method and limitations of researches in this area were also summarized. Eight databases were searched from their inception dates to February 2020. Nineteen eligible studies containing 21 comparisons were identified ultimately. The risk of bias and data on outcome measures were analyzed by the CAMARADES 10-item checklist and Rev-Man 5.3 software separately. The results displayed the number of criteria met varied from 3/10 to 7/10 with an average of 5.05. The present study provided the preliminary preclinical evidence that oral administration of Q or its derivatives was capable of improving bone pathology, bone-related parameters under imageology and bone maximum load, increasing serum osteocalcin, alkaline phosphatase, and estradiol, and reducing serum c-terminal cross-linked telopeptide of type I collagen (P < 0.05). No statistical difference was seen in survival rate, index of liver, or kidney function (P > 0.05). Q and its derivatives partially reverse osteopenia probably via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, promoting osteogenesis, inhibiting osteoclasts, and its estrogen-like effect. The findings reveal the possibility of developing Q or its derivatives as a drug or an ingredient in diet for clinical treatment of osteoporosis.
Copyright © 2020 Yue-Yue Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this study.
Figures

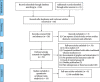
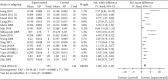








Similar articles
-
Oral administration of quercetin inhibits bone loss in rat model of diabetic osteopenia.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov 16;670(1):317-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.014. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21914440
-
CD109 deficiency induces osteopenia with an osteoporosis-like phenotype in vivo.Genes Cells. 2018 Jul;23(7):590-598. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12593. Epub 2018 May 16. Genes Cells. 2018. PMID: 29767469
-
Alendronate reduces serum TNFalpha and IL-1beta, increases neutrophil counts, and improves bone mineral density and bone metabolism indices in patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia (CIN)-associated osteopenia/osteoporosis.J Bone Miner Metab. 2004;22(6):577-87. doi: 10.1007/s00774-004-0526-y. J Bone Miner Metab. 2004. PMID: 15490268 Clinical Trial.
-
[A Novel Oral Anti-osteoporosis Drug with Osteogenesis-promoting Effects via Osteoblast Differentiation].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):19-25. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00154-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606923 Review. Japanese.
-
Prevalence of osteoporosis and osteopenia in men and premenopausal women with celiac disease: a systematic review.Nutr J. 2019 Feb 7;18(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12937-019-0434-6. Nutr J. 2019. PMID: 30732599 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Application of Citrus and Apple Fibers for Formulation of Quercetin/Fiber Aggregates: Impact of Quercetin Concentration.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;11(24):3582. doi: 10.3390/plants11243582. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559694 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Osteogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Synergistic Effect of Orthosilicic Acid, Vitamin K2, Curcumin, Polydatin and Quercetin Combination in Young and Senescent Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 16;24(10):8820. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108820. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240169 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisia scoparia and Metabolic Health: Untapped Potential of an Ancient Remedy for Modern Use.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 8;12:727061. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.727061. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35211087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Elucidate the Pharmacological Mechanism of the OSTEOWONDER Capsule for Treating Osteoporosis.Front Genet. 2022 Feb 28;13:833027. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.833027. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35295951 Free PMC article.
-
Icariin attenuates thioacetamide‑induced bone loss via the RANKL‑p38/ERK‑NFAT signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Apr;25(4):126. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12642. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35169865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geng Z., Xu L. L., Zhang X. Y., Wang Y. G. Effects of rutin on the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis. 2019;25:497–501.
-
- Evans R. K., Negus C. H., Centi A. J., Spiering B. A., Kraemer W. J., Nindl B. C. Peripheral QCT sector analysis reveals early exercise induced increases in tibial bone mineral density. Journal of Musculoskeletal & Neuronal Interactions. 2012;12(3):155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

