Lumbosacral extradural extramedullary hematopoiesis in thalassemia major causing spinal canal stenosis
- PMID: 33194265
- PMCID: PMC7656047
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_563_2020
Lumbosacral extradural extramedullary hematopoiesis in thalassemia major causing spinal canal stenosis
Abstract
Background: Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EH) is common in patients with ineffective erythropoiesis like thalassemia major (TM). EH commonly involves intra-abdominal organs (e.g., spleen and liver), but rarely involves vertebral bodies. Here, we reviewed images of EH contributing to spinal canal stenosis.
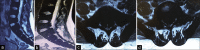
Case description: A 19-year-old male with beta-thalassemia major (TM) presented with pain and bilateral lower extremity neurogenic claudication. Bilaterally, on examination, he had positive straight leg raising to 30°, a loss of the Achilles responses, and decreased pain appreciation in the L5S1 distributions. The lumbar MR showed anterior epidural lobulated mass lesions at L5 and S1, contributing to marked canal stenosis. Following an L5/S1 laminectomy for decompression, the biopsy revealed extramedullary hematopoietic tissue.
Conclusion: Patients presenting with the lower extremity symptoms/signs, ranging from low back pain to neurogenic claudication and even paraplegia, may have EH secondary to TM. Treatment options include hypertransfusion, local radiation therapy, and/or surgical decompression.
Keywords: Beta-thalassemia; Extramedullary hematopoiesis; Radiculopathy; Spinal stenosis.
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long segment spinal epidural extramedullary hematopoiesis.Surg Neurol Int. 2013 Dec 26;4:161. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.123657. eCollection 2013. Surg Neurol Int. 2013. PMID: 24404404 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial extramedullary hematopoiesis in patients with thalassemia: a case report and review of the literature.Transfusion. 2012 Aug;52(8):1715-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03499.x. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Transfusion. 2012. PMID: 22220514 Review.
-
Curable paraplegia due to extradural hematopoietic tissue in thalassemia.Neurosurgery. 1982 Dec;11(6):804-7. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198212000-00017. Neurosurgery. 1982. PMID: 7162576
-
Successful operative management of an upper lumbar spinal canal stenosis resulting in multilevel lower nerve root radiculopathy.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015 Jan;6(1):108-11. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.143216. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015. PMID: 25552866 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive spinal cord compression due to epidural extramedullary hematopoiesis in thalassemia intermedia. A case report and literature review.Neuroradiol J. 2013 Feb;26(1):111-7. doi: 10.1177/197140091302600119. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Neuroradiol J. 2013. PMID: 23859178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amirjamshidi A, Abbassioun K, Ketabchi S. Spinal extradural hematopoiesis in adolescents with thalassemia. Childs Nerv Syst. 1991;7:223–5. - PubMed
-
- Chehal A, Aoun E, Koussa S, Skoury H, Koussa S, Taher A. Hypertransfusion: A successful method of treatment in thalassemia intermedia patients with spinal cord compression secondary to extramedullary hematopoiesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003;28:E245–9. - PubMed
-
- Munn RK, Kramer CA, Arnold SM. Spinal cord compression due to extramedullary hematopoiesis in beta-thalassemia intermedia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42:607–9. - PubMed
-
- Taher A, Isma’eel H, Cappellini MD. Thalassemia intermedia: Revisited. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2006;37:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Taher A, Vichinsky EP, Musallam K, Cappellini MD, Viprakasit V, Thalassaemia International F. Cyprus: Thalassaemia International Federation; 2013. Guidelines for the Management of Non Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia (NTDT) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
