Rare Presentation of Toxoplasma Pneumonitis in the Absence of Neurological Symptoms in an AIDS Patient and Use of Next-Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis
- PMID: 33194865
- PMCID: PMC7655009
- DOI: 10.12890/2020_001862
Rare Presentation of Toxoplasma Pneumonitis in the Absence of Neurological Symptoms in an AIDS Patient and Use of Next-Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis
Abstract
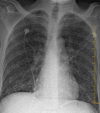
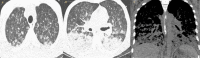
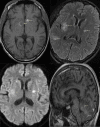
Toxoplasma gondii is a known cause of encephalitis in human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) patients. Toxoplasma pneumonitis is a manifestation of extracerebral toxoplasmosis and can be clinically indistinguishable from other opportunistic infections including Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) and miliary tuberculosis. In this case report, Toxoplasma pneumonitis and disseminated toxoplasmosis was diagnosed using next-generation sequencing (NGS) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assessment. NGS can detect microbial cell-free DNA (cfDNA) circulating in the plasma of over 1,000 pathogens. This case is a rare presentation of Toxoplasma pneumonitis in the absence of neurological symptoms and we discuss the use of NGS of microbial cfDNA and PCR tests that may be utilized for the timely diagnosis of such challenging cases.
Learning points: Next-generation sequencing can help make a correct diagnosis and detect culture-negative opportunistic infections.Recognition of Toxoplasma pneumonitis as a rare presentation of disseminated toxoplasmosis.In cases of Toxoplasma pneumonitis, brain imaging should be conducted to rule out CNS involvement even in the absence of neurological symptoms.
Keywords: AIDS; Disseminated toxoplasmosis; Toxoplasma pneumonitis, next-generation sequencing, HIV.
© EFIM 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing as a diagnostic tool for toxoplasmic encephalitis.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018 Dec 26;17(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12941-018-0298-1. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018. PMID: 30587202 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma pneumonitis: fatal presentation of disseminated toxoplasmosis in a patient with AIDS.Eur Respir J. 1992 Sep;5(8):1018-20. Eur Respir J. 1992. PMID: 1426192
-
Pneumocystis pneumonia and rheumatic disease: diagnostic potential of circulating microbial cell-free DNA sequencing.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2021 Dec 27;6(1):rkab105. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkab105. eCollection 2022. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2021. PMID: 35028498 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord toxoplasmosis in human immunodeficiency virus infection/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.Infect Dis (Lond). 2015 May;47(5):277-82. doi: 10.3109/00365548.2014.993421. Infect Dis (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25835092 Review.
-
Neurological manifestations of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): experience at UCSF and review of the literature.J Neurosurg. 1985 Apr;62(4):475-95. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.4.0475. J Neurosurg. 1985. PMID: 2983051 Review.
Cited by
-
A case of tick-transmitted Q fever in Lishui, China diagnosed by next-generation sequencing.J Int Med Res. 2021 Sep;49(9):3000605211025398. doi: 10.1177/03000605211025398. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34590876 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Mpox Virus Using Microbial Cell-Free DNA: The Potential of Pathogen-Agnostic Sequencing for Rapid Identification of Emerging Pathogens.J Infect Dis. 2024 Mar 26;229(Supplement_2):S144-S155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad452. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37824825 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: A toxoplasmic encephalitis in an immunocompromised child detected through metagenomic next-generation sequencing.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 28;11:1247233. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1247233. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37841727 Free PMC article.
-
In defense of children's brain: reshuffling the laboratory toolbox for the diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2024 Jun 12;62(6):e0169723. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01697-23. Epub 2024 May 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38780287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariuz P, Bosler EM, Luft BJ. Toxoplasma pneumonia. Semin Respir Infect. 1997;12(1):40–43. - PubMed
-
- Schnapp LM, Geaghan SM, Campagna A, Fahy J, Steiger D, Ng V, et al. Toxoplasma gondii pneumonitis in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(5):1073–1077. - PubMed
-
- Bergin C, Murphy M, Lyons D, Gaffney E, Mulcahy FM. Toxoplasma pneumonitis: fatal presentation of disseminated toxoplasmosis in a patient with AIDS. Eur Respir J. 1992;5(8):1018–1020. - PubMed
-
- Oksenhendler E, Cadranel J, Sarfati C, Katlama C, Datry A, Marche C, et al. Toxoplasma gondii pneumonia in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1990;88(5N):18N–21N. - PubMed
-
- Murat JB, Hidalgo HF, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Pelloux H. Human toxoplasmosis: which biological diagnostic tests are best suited to which clinical situations? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013;11(9):943–956. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
