Correlation of Clinical Findings in Acute Spinal Injury Patients with Magnetic Resonance Including Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Fiber Tractography
- PMID: 33195854
- PMCID: PMC7661030
- DOI: 10.22603/ssrr.2020-0048
Correlation of Clinical Findings in Acute Spinal Injury Patients with Magnetic Resonance Including Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Fiber Tractography
Abstract
Introduction: Many types of research are being carried out in the fields of understanding of the pathogenesis, early recognition, and improving the outcomes after spinal cord injury (SCI). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is one of the modalities used in vivo microstructural assessment of SCI. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the role of DTI imaging and fiber tractography in acute spinal injury with clinical profile and neurological outcome.
Methods: The study was carried out on twenty-five patients of acute spinal cord injury who presented within 48 hours of injury and completed minimum of six months follow-up.
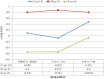
Results: The mean age of patients was 37.32±13.31 years and male & female ratio of 18:7. Total MIS score was 91.64±6.0 initially which improved to 96.92±3.68 after 3 months and 99.4±1.35 after 6 months. Total SIS score was similar at all the time intervals i.e. 224±0. Maximum subjects 14(56%) were classified into AIS C and 5(20%) into AIS D whereas only 6(24%) subjects were having no deficit (AIS E). At the end of 6 months, 13(52%) subjects had no deficit (AIS E). Mean fractional anisotropy (FA) initially was 0.451 (± 0.120) but after 6 months, it increased to 0.482 (± 0.097) (p<0.001). The mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) initially was 3.13 (± 2.68) but after 6 months, it decreased to 3.06 (± 2.68) and this change was found to be statistically highly significant (p<0.001). Mean anisotropy index (AI) initially was 0.420 (± 0.245) but after 6 months, it increased to 0.430 (± 3.41) and this change was found to be statistically significant (p<0.01).
Conclusions: DTI is a sensitive tool to detect neurological damage in SCI and subsequent neurological recovery. FA correlated with ASIA impairment scale. It can be useful as an adjunct to conventional MRI for better evaluation and predicting prognosis in SCI patients.
Keywords: Acute spinal cord injury; Diffusion Tensor Imaging; Fiber Tractography; Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Copyright © 2020 by The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that there are no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Fujiyoshi K, Konomi T, Yamada M, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of the spinal cord: from experimental studies to clinical application. Exp Neurol. 2013;242(4):74-82. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Zhou C, Zhu L, et al. Identifying the injury in demyelinating cervical spinal cord disease: A diffusion tensor imaging and tractography study. Neurol Asia. 2016;21(1):73-80.
-
- Bhattia V. Diffusion tractography in spinal cord injury: preliminary experience. Pak J Neurol Sci. 2012;7(2):14-6.
-
- Sandler AN, Tator CH. Review of the effect of spinal cord trauma on the vessels and blood flow in the spinal cord. J Neurosurg. 1976;45(6):638-46. - PubMed
-
- Wagner Jr FC, Dohrmann GJ, Bucy PC. Histopathology of transitory traumatic paraplegia in the monkey. J Neurosurg. 1971;35(3):272-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
