Combining chemotherapy and autologous peptide-pulsed dendritic cells provides survival benefit in stage IV melanoma patients
- PMID: 33197129
- PMCID: PMC7756560
- DOI: 10.1111/ddg.14334
Combining chemotherapy and autologous peptide-pulsed dendritic cells provides survival benefit in stage IV melanoma patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: We examined retrospectively whether the combination of standard dacarbazine (DTIC) and/or fotemustine chemotherapy and autologous peptide-loaded dendritic cell (DC) vaccination may improve survival of stage IV melanoma patients. Furthermore, a small cohort of long-term survivors was studied in more detail.
Patients and methods: Between 1998 and 2008, 41 patients were vaccinated at least three times with DCs while receiving chemotherapy and compared to all other 168 patients in our database who only received chemotherapy (1993-2008).
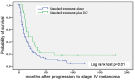
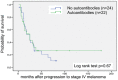
Results: Median life expectancy of patients receiving additional DC-vaccination was 18 months, compared to eleven months for patients under standard chemotherapy alone. In contrast to patients with other haplotypes, the HLA-A1/A1 subset of DC-treated patients showed significantly lower median survival (12 vs. 25 months). Autoantibodies were frequently detected in serum of both vaccinated and non-vaccinated patients, and there was no correlation between titers, loss or appearance of autoantibodies and survival. Additionally, phenotyping of DCs and PBMCs also did not reveal any conspicuous correlation with survival.
Conclusions: Combining standard chemotherapy and DC vaccination appears superior to chemotherapy alone. The impact of HLA haplotypes on survival emphasizes the importance of a careful selection of patients with specific, well-defined HLA haplotypes for future vaccination trials using peptide-pulsed DCs, possibly combined with checkpoint inhibitors.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Deutsche Dermatologische Gesellschaft.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dacarbazine (DTIC) versus vaccination with autologous peptide-pulsed dendritic cells (DC) in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma: a randomized phase III trial of the DC study group of the DeCOG.Ann Oncol. 2006 Apr;17(4):563-70. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdj138. Epub 2006 Jan 17. Ann Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16418308 Clinical Trial.
-
Peptide-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy for stage IV melanoma.Melanoma Res. 2017 Aug;27(4):326-334. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000342. Melanoma Res. 2017. PMID: 28263240 Clinical Trial.
-
Immune and clinical outcomes in patients with stage IV melanoma vaccinated with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells derived from CD34+ progenitors and activated with type I interferon.J Immunother. 2005 Sep-Oct;28(5):505-16. doi: 10.1097/01.cji.0000171292.79663.cb. J Immunother. 2005. PMID: 16113607 Clinical Trial.
-
Adjuvant vaccination with melanoma antigen-pulsed dendritic cells in stage III melanoma patients.Med Oncol. 2012 Dec;29(4):2966-77. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0168-1. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22302285
-
Dendritic cell gene therapy.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2002 Jul;11(3):645-60. doi: 10.1016/s1055-3207(02)00027-3. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2002. PMID: 12487060 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances and Challenges in Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;14(16):3972. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163972. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cancer Immunotherapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 1;15(8):2070. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082070. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances and Future Perspective of DC-Based Therapy in NSCLC.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 28;12:704776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.704776. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34262573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krensel M, Petersen J, Mohr P et al. Estimating prevalence and incidence of skin cancer in Germany. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2019; 17: 1239–49. - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB. The treatment of metastatic melanoma with chemotherapy and biologics. Curr Opin Oncol 1997; 9: 205–13. - PubMed
-
- Eigentler TK, Caroli UM, Radny P et al. Palliative therapy of disseminated malignant melanoma: a systematic review of 41 randomised clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 2003; 4: 748–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

