Engineering of a functional γ-tocopherol transfer protein
- PMID: 33197771
- PMCID: PMC7677715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101773
Engineering of a functional γ-tocopherol transfer protein
Abstract
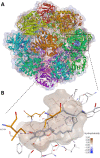
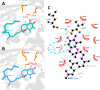
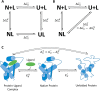
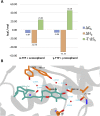
α-tocopherol transfer protein (TTP) was previously reported to self-aggregate into 24-meric spheres (α-TTPS) and to possess transcytotic potency across mono-layers of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). In this work, we describe the characterisation of a functional TTP variant with its vitamer selectivity shifted towards γ-tocopherol. The shift was obtained by introducing an alanine to leucine substitution into the substrate-binding pocket at position 156 through site directed mutagenesis. We report here the X-ray crystal structure of the γ-tocopherol specific particle (γ-TTPS) at 2.24 Å resolution. γ-TTPS features full functionality compared to its α-tocopherol specific parent including self-aggregation potency and transcytotic activity in trans-well experiments using primary HUVEC cells. The impact of the A156L mutation on TTP function is quantified in vitro by measuring the affinity towards γ-tocopherol through micro-differential scanning calorimetry and by determining its ligand-transfer activity. Finally, cell culture experiments using adherently grown HUVEC cells indicate that the protomers of γ-TTP, in contrast to α-TTP, do not counteract cytokine-mediated inflammation at a transcriptional level. Our results suggest that the A156L substitution in TTP is fully functional and has the potential to pave the way for further experiments towards the understanding of α-tocopherol homeostasis in humans.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Cytokine; Nanoparticle; Transcytosis; Vitamin E.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ingold K., Webb A., Witter D., Burton G., Metcalfe T., Muller D. Vitamin e remains the major lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant in human plasma even in individuals suffering severe vitamin e deficiency. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987;259(1):224–225. - PubMed
-
- Grusak M.A., DellaPenna D. Improving the nutrient composition of plants to enhance human nutrition and health 1. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1999;50(1):133–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

