Immune-related biomarker risk score predicts prognosis in prostate cancer
- PMID: 33197890
- PMCID: PMC7746334
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103921
Immune-related biomarker risk score predicts prognosis in prostate cancer
Abstract
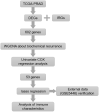
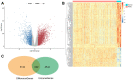
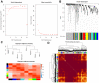
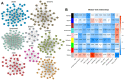
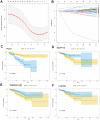
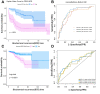
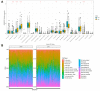
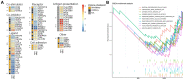
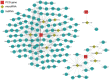
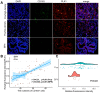
In this study, we constructed a model using a Cox proportional hazards model based on the expression of eight immune-related genes that were associated with prognosis in prostate cancer: EDNRB, ANGPTL2, TNFSF15, TNFRSF10D, EDN2, BMP2, NLRP14, and PLK1. We then identified associations between risk scores calculated with the model, tumor microenvironment characteristics, and immune cell infiltration. Prostate cancer patients in the high score group had poorer prognoses, and validation with the external GSE54460 dataset confirmed that the scoring model predicted biochemical recurrence with AUC values of 0.749 at 1 year, 0.804 at 3 years, and 0.774 at 5 years. Proportions of infiltrated M2 macrophages and regulatory T cells were increased in the high risk group, while CD8+ T cells were increased in the low risk group. Network analysis revealed that PLK1 may be a key regulator of the immune-suppressive microenvironment in prostate cancer. Double immunofluorescence labeling of a prostate cancer tissue microarray indicated that PLK1 expression correlated positively with numbers of infiltrating macrophages. These results indicate that an immune- related, gene-based risk score effectively reflects immune microenvironment characteristics and predicts prognosis in prostate cancer.
Keywords: PLK1; immune microenvironment; immune-related genes; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Antonarakis ES, Piulats JM, Gross-Goupil M, Goh J, Ojamaa K, Hoimes CJ, Vaishampayan U, Berger R, Sezer A, Alanko T, de Wit R, Li C, Omlin A, et al. Pembrolizumab for treatment-refractory metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: multicohort, open-label phase II KEYNOTE-199 study. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38:395–405. 10.1200/JCO.19.01638 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gao J, Ward JF, Pettaway CA, Shi LZ, Subudhi SK, Vence LM, Zhao H, Chen J, Chen H, Efstathiou E, Troncoso P, Allison JP, Logothetis CJ, et al. VISTA is an inhibitory immune checkpoint that is increased after ipilimumab therapy in patients with prostate cancer. Nat Med. 2017; 23:551–55. 10.1038/nm.4308 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

