Serum KIAA1199 is an advanced-stage prognostic biomarker and metastatic oncogene in cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 33197891
- PMCID: PMC7762501
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103964
Serum KIAA1199 is an advanced-stage prognostic biomarker and metastatic oncogene in cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Cell proliferation and migration are the determinants of malignant tumor progression, and a better understanding of related genes will lead to the identification of new targets aimed at preventing the spread of cancer. Some studies have shown that KIAA1199 (CEMIP) is a transmembrane protein expressed in many types of noncancerous cells and cancer cells. However, the potential role of KIAA1199 in the progression of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) remains unclear.
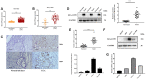
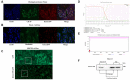
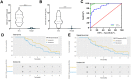
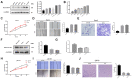
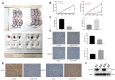
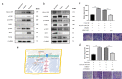
Results: Analysis of cancer-related databases showed that KIAA1199 is overexpressed in CCA. ELISA, immunohistochemistry, Western blotting and qPCR indicated high expression levels of KIAA1199 in serum, CCA tissues and CCA cell lines. In the serum (n = 41) and large sample validation (n = 177) cohorts, higher KIAA1199 expression was associated with shorter overall survival and disease-free survival times. At the cellular level, KIAA1199 overexpression (OE) promoted CCA growth and metastasis. Subcutaneous tumor xenograft experiments showed that KIAA1199 enhances CCA cell proliferation. Additionally, the expression levels of components in the EMT-related TGF-β pathway changed significantly after KIAA1199 upregulation and silencing.
Conclusion: KIAA1199 is a promising new diagnostic molecule and therapeutic target in CCA. The serum KIAA1199 level can be used as a promising clinical tool for predicting the overall postoperative outcomes of patients with CCA.
Methods: CCA-related KIAA1199 data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databases. To assess the prognostic impact of KIAA1199, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the serum level of KIAA1199 in 41 patients who underwent surgical resection. Immunohistochemical staining, Western blotting and qPCR were used to verify and retrospectively review the expression levels of KIAA1199 in cancer tissue specimens from 177 CCA patients. The effect of KIAA1199 on CCA was evaluated by cell-based functional assays and subcutaneous tumor xenograft experiments. The expression levels of proteins associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and activation of relevant signaling pathways were measured via Western blotting.
Keywords: KIAA1199; bile; biomarker; cholangiocarcinoma; serum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
KIAA1199 promotes invasion and migration in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) via PI3K-Akt mediated EMT.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Jan;97(1):127-140. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1721-y. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30478628
-
Knockdown of tripartite motif 59 (TRIM59) inhibits proliferation in cholangiocarcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.044. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30822475
-
Up-regulated LINC00261 predicts a poor prognosis and promotes a metastasis by EMT process in cholangiocarcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Jan;216(1):152733. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152733. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 31812439
-
The emerging role of KIAA1199 in cancer development and therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111507. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111507. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33773462 Review.
-
The Role of microRNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 16;22(14):7627. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147627. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299246 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of CEMIP in cancers and its transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.PeerJ. 2024 Feb 19;12:e16930. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16930. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38390387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glioblastoma progression is hindered by melatonin-primed mesenchymal stromal cells through dynamic intracellular and extracellular reorganizations.Theranostics. 2025 Feb 10;15(7):3076-3097. doi: 10.7150/thno.104143. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40083939 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-enhanced insights into sphingolipid-based prognostication: revealing the immunological landscape and predictive proficiency for immunomotherapy and chemotherapy responses in pancreatic carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Oct 31;10:1284623. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1284623. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38028544 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of CEMIP Correlates Poor Prognosis and the Tumur Microenvironment in Breast Cancer as a Promisingly Prognostic Biomarker.Front Genet. 2021 Dec 13;12:768140. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.768140. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34966410 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of microfibrillar-associated protein 2 is closely associated with tumor angiogenesis and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2021 Oct;22(4):739. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13000. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34466151 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

