CD138- multiple myeloma cells express high level of CHK1 which correlated to overall survival in MM patient
- PMID: 33197893
- PMCID: PMC7746343
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.104066
CD138- multiple myeloma cells express high level of CHK1 which correlated to overall survival in MM patient
Abstract
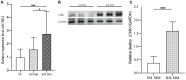
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a disease in which abnormal plasma cells proliferate and secrete monoclonal immunoglobulin in the bone marrow. The main characteristic of plasma cells is the expression of the cell surface antigen syndecan-1 (CD138). However, the expression of CD138 is limited to terminally differentiated plasma cells during B cell development. A small subpopulation (2~5%) of human MM cells that lack CD138 expression has been shown to possess enormous proliferation potential in vitro experiment and in animal models, and they also can differentiate into CD138+ plasma cells. Thus, this small subset of MM cells was regarded as myeloma cancer stem cell (MCSC). However, its characteristics associated with the pathogenesis of MM remain unclear. In this study, we analyzed the gene expression data of CD138 cell lines downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Limma package in RStudio was used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Genes enrichment and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis were performed on DAVID and STRING databases. Furthermore, overall survival (OS) analysis in MM patient was utilized to screen out the hub-genes closely associate with the MM pathogenesis process. Hub-genes expression validation and receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was performed in different stages of plasma cell disorder diseases. Finally, we verified these findings in MM patient samples. Through integrated bioinformatics analysis of MM CD138- and CD138+ cell lines, we found that CDC7, CDK1, and CHK1 are highly expressed in CD138- MM cells. These genes are crucial in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle pathway, which is closely related to the malignant proliferation in various tumor cells. Of note, we found that patients with high expression of CDC7, CDK1, and CHK1 had shorter overall survival time. The expression of CHK1 was significantly increased in MM cells compared with normal plasma cell (NPC) and MGUS. More importantly, we further clarified that the expression of CHK1 in release/refraction MM (R/R MM) has obviously increased compared with new diagnosed MM (ND MM).
Keywords: CD138; CHK1; bioinformatics; cancer stem cell; multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
High expression of VARS promotes the growth of multiple myeloma cells by causing imbalance in valine metabolism.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Jun 28;48(6):795-808. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220602. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37587064 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
CD138-negative myeloma cells regulate mechanical properties of bone marrow stromal cells through SDF-1/CXCR4/AKT signaling pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1853(2):338-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25450979 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia reduces CD138 expression and induces an immature and stem cell-like transcriptional program in myeloma cells.Int J Oncol. 2013 Dec;43(6):1809-16. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2134. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24126540 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecan-1 and stromal heparan sulfate proteoglycans: key moderators of plasma cell biology and myeloma pathogenesis.Blood. 2021 Apr 1;137(13):1713-1718. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008188. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33512430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strong Correlation between the Expression of CHEK1 and Clinicopathological Features of Patients with Multiple Myeloma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020;30(4):349-357. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2020027084. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020. PMID: 32894664 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of CD20 combined with CD138 positive expression in patients with chronic endometritis.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Jun 15;14(3):145-156. doi: 10.62347/LIHI3143. eCollection 2025. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40689313 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of a Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature in Patients With Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 1;9:739011. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.739011. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34790661 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of fatty acid metabolism-related genes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 13;13(13):17847-17863. doi: 10.18632/aging.203288. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34257161 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of multiple myeloma patients based on histopathological evaluation of bone marrow.Caspian J Intern Med. 2025 Jun 23;16(3):562-569. doi: 10.22088/cjim.16.3.562. eCollection 2025 Summer. Caspian J Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40786573 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy for multiple myeloma: an overview on CD138-based strategies.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 9;14:1370854. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1370854. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38655136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao WH, Liu J, Wang BY, Chen YX, Cao XM, Yang Y, Zhang YL, Wang FX, Zhang PY, Lei B, Gu LF, Wang JL, Yang N, et al.. A phase 1, open-label study of LCAR-B38M, a chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy directed against B cell maturation antigen, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Hematol Oncol. 2018; 11:141. 10.1186/s13045-018-0681-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

