Biological Activity of Berberine-A Summary Update
- PMID: 33198257
- PMCID: PMC7697704
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12110713
Biological Activity of Berberine-A Summary Update
Abstract
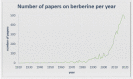
Berberine is a plant metabolite belonging to the group of isoquinoline alkaloids with strong biological and pharmacological activity. Currently, berberine is receiving considerable interest due to its anticancer activity based on many biochemical pathways, especially its proapoptotic and anti-inflammatory activity. Therefore, the growing number of papers on berberine demands summarizing the knowledge and research trends. The efficacy of berberine in breast and colon cancers seems to be the most promising aspect. Many papers focus on novel therapeutic strategies based on new formulations or search for new active derivatives. The activity of berberine is very important as regards sensitization and support of anticancer therapy in combination with well-known but in some cases inefficient therapeutics. Currently, the compound is being assessed in many important clinical trials and is one of the most promising and intensively examined natural agents.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; berberine; bioavailability; clinical trials; metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barrios V., Escobar C., Cicero A.F.G., Burke D., Fasching P., Banach M., Bruckert E. A nutraceutical approach (Armolipid Plus) to reduce total and LDL cholesterol in individuals with mild to moderate dyslipidemia: Review of the clinical evidence. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2017;24:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2016.10.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources