Optimization of the Biocatalysis for D-DIBOA Synthesis Using a Quick and Sensitive New Spectrophotometric Quantification Method
- PMID: 33198293
- PMCID: PMC7697731
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21228523
Optimization of the Biocatalysis for D-DIBOA Synthesis Using a Quick and Sensitive New Spectrophotometric Quantification Method
Abstract
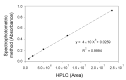
D-DIBOA (4-hydroxy-(2H)-1,4-benzoxazin-3-(4H)-one) is an allelopathic-derived compound with interesting herbicidal, fungicidal, and insecticide properties whose production has been successfully achieved by biocatalysis using a genetically engineered Escherichia coli strain. However, improvement and scaling-up of this process are hampered by the current methodology for D-DIBOA quantification, which is based on high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC), a time-consuming technique that requires expensive equipment and the use of environmentally unsafe solvents. In this work, we established and validated a rapid, simple, and sensitive spectrophotometric method for the quantification of the D-DIBOA produced by whole-cell biocatalysis, with limits of detection and quantification of 0.0165 and 0.0501 µmol·mL-1 respectively. This analysis takes place in only a few seconds and can be carried out using 100 µL of the sample in a microtiter plate reader. We performed several whole-cell biocatalysis strategies to optimize the process by monitoring D-DIBOA production every hour to keep control of both precursor and D-DIBOA concentrations in the bioreactor. These experiments allowed increasing the D-DIBOA production from the previously reported 5.01 mM up to 7.17 mM (43% increase). This methodology will facilitate processes such as the optimization of the biocatalyst, the scaling up, and the downstream purification.
Keywords: D-DIBOA; nitroreductase NfsB; spectrophotometric method; whole-cell biocatalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Figures





References
-
- Rimando A.M., Duke S.O. Natural Products for Pest Management. ACS Publications; Washington, DC, USA: 2006. pp. 2–21.
-
- Macías F.A., Marín D., Oliveros-Bastidas A., Castellano D., Simonet A.M., Molinillo J.M.G. Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Studies of Benzoxazinones, Their Degradation Products, and Analogues. Phytotoxicity on Problematic Weeds Avena fatua L. and Lolium rigidum Gaud. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006;54:1040–1048. doi: 10.1021/jf050903h. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Macías F.A., Marín D., Oliveros-Bastidas A., Castellano D., Simonet A.M., Molinillo J.M.G. Structure−Activity Relationships (SAR) studies of benzoxazinones, their degradation products and analogues. Phytotoxicity on standard target species (STS) J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005;53:538–548. doi: 10.1021/jf0484071. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

