Combination therapy of ginsenoside compound K and methotrexate was efficient in elimination of anaemia and reduction of disease activity in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats
- PMID: 33198544
- PMCID: PMC7671656
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1844761
Combination therapy of ginsenoside compound K and methotrexate was efficient in elimination of anaemia and reduction of disease activity in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats
Abstract
Context: Ginsenoside compound K (CK) has anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, and myelosuppressive protective effects. Methotrexate (MTX) is widely used in combination therapy for rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objective: To evaluate the effects of combination therapy of CK and MTX on anaemia and anti-arthritis in adjuvant-induced arthritis (AA) rats.
Materials and methods: AA was induced in rats by Complete Freund's adjuvant, and divided into five groups (n = 10): normal, AA, CK 80 mg/kg, combination therapy (80 mg/kg CK combined with 0.5 mg/kg MTX), and MTX 0.5 mg/kg. From day 12, CK (once a day for 15 days) or MTX (once every 3 days, five times) were intragastrically administered.
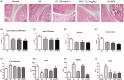
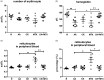
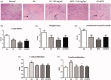
Results: Combination therapy showed increased haemoglobin to 148.5 ± 10.1 g/L compared with AA (129.8 ± 11.7 g/L) and MTX (128.8 ± 18.4 g/L), and decreased reticulocytes in peripheral blood to 4.9 ± 1.1% compared with MTX (9.3 ± 3.3%). In combination therapy group, paw swelling decreased to 5.6 ± 4.3 mL compared with CK (9.4 ± 3.9 mL) and MTX (13.5 ± 7.4 mL), and swollen joint count decreased to 1.4 ± 0.8 compared with CK (2.1 ± 1.0) and MTX (2.4 ± 1.2) at day 24. Combination therapy showed decreased IL-6 to 25.1 ± 17.2 pg/mL compared with MTX (44.9 ± 4.8 pg/mL), and decreased IL-17 to 5.8 ± 3.9 pg/mL compared with MTX (10.7 ± 4.2 pg/mL).
Conclusion: The anti-anaemia effect of CK deserves further study, and CK can be a candidate effective drug for combined treatment in RA with anaemia.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis; anaemia of inflammation; natural products of ginsenosides.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Chen J, Wang Q, Wu H, Liu K, Wu Y, Chang Y, Wei W.. 2016. The ginsenoside metabolite compound K exerts its anti-inflammatory activity by down regulating memory B cell in adjuvant-induced arthritis. Pharm Biol. 54(7):1280–1288. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Wu H, Wang Q, Chang Y, Liu K, Song S, Yuan P, Fu J, Sun W, Huang Q, et al. 2014. Ginsenoside metabolite compound k alleviates adjuvant-induced arthritis by suppressing T cell activation. Inflammation. 37(5):1608–1615. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Wu H, Wang Q, Chang Y, Liu K, Wei W.. 2015. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K suppresses T-cell priming via modulation of dendritic cell trafficking and costimulatory signals, resulting in alleviation of collagen-induced arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 353(1):71–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
