The D614G mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Implications for viral infectivity, disease severity and vaccine design
- PMID: 33199022
- PMCID: PMC7643658
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.109
The D614G mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Implications for viral infectivity, disease severity and vaccine design
Abstract
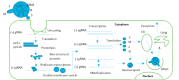
The development of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has prompted an extensive worldwide sequencing effort to characterise the geographical spread and molecular evolution of the virus. A point mutation in the spike protein, D614G, emerged as the virus spread from Asia into Europe and the USA, and has rapidly become the dominant form worldwide. Here we review how the D614G variant was identified and discuss recent evidence about the effect of the mutation on the characteristics of the virus, clinical outcome of infection and host immune response.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Mutation; Neutralising antibody; SARS-CoV-2; Spike.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sui J., Aird D.R., Tamin A., Murakami A., Yan M., Yammanuru A., Jing H., Kan B., Liu X., Zhu Q., Yuan Q.A., Adams G.P., Bellini W.J., Xu J., Anderson L.J., Marasco W.A. Broadening of neutralization activity to directly block a dominant antibody-driven SARS-coronavirus evolution pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000197. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fauver J.R., Petrone M.E., Hodcroft E.B., Shioda K., Ehrlich H.Y., Watts A.G., Vogels C.B.F., Brito A.F., Alpert T., Muyombwe A., Razeq J., Downing R., Cheemarla N.R., Wyllie A.L., Kalinich C.C., Ott I.M., Quick J., Loman N.J., Neugebauer K.M., Greninger A.L., Jerome K.R., Roychoudhury P., Xie H., Shrestha L., Huang M.L., Pitzer V.E., Iwasaki A., Omer S.B., Khan K., Bogoch, Martinello R.A., Foxman E.F., Landry M.L., Neher R.A., Ko A.I., Grubaugh N.D. Coast-to-Coast spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the early epidemic in the United States. Cell. 2020;181:990–996. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.021. e995. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Korber B., Fischer W.M., Gnanakaran S., Yoon H., Theiler J., Abfalterer W., Hengartner N., Giorgi E.E., Bhattacharya T., Foley B., Hastie K.M., Parker M.D., Partridge D.G., Evans C.M., Freeman T.M., de Silva T.I., Sheffield C.-G.G., McDanal C., Perez L.G., Tang H., Moon-Walker A., Whelan S.P., LaBranche C.C., Saphire E.O., Montefiori D.C. Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell. 2020;182:812–827 e819. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

